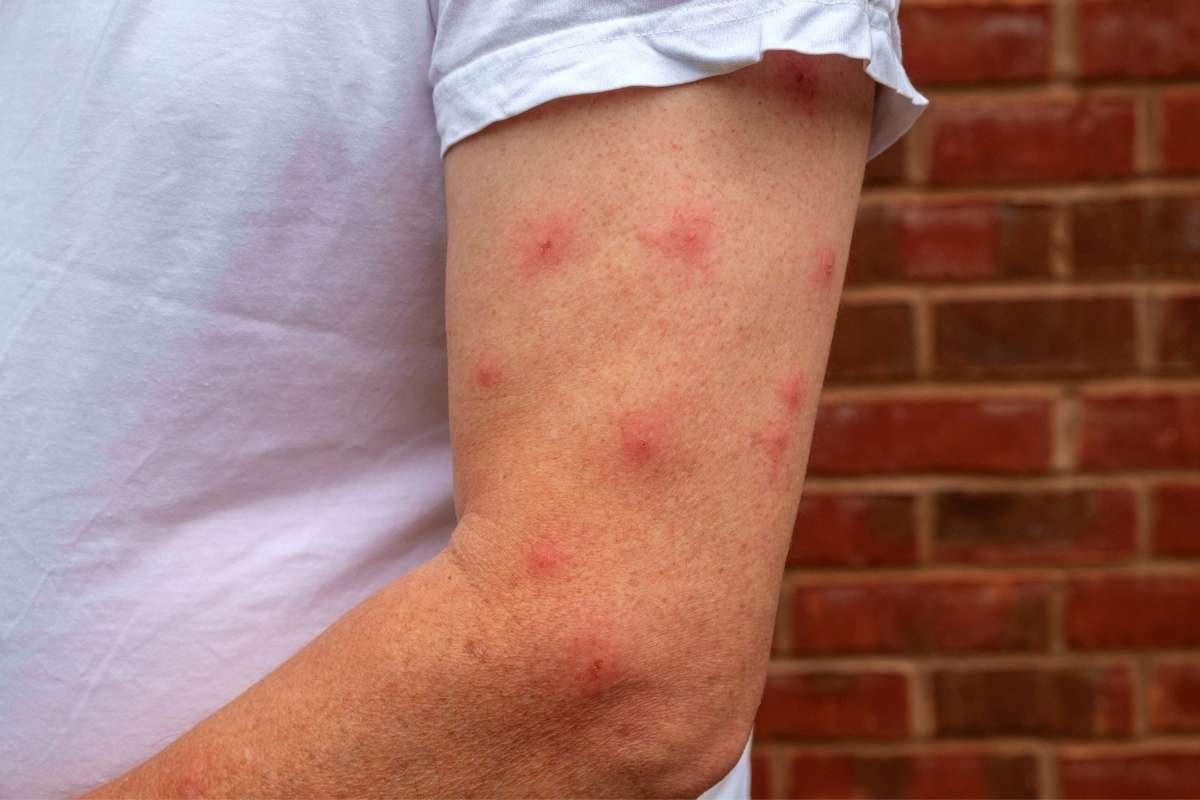
Autoimmune skin disorders is a disease that occurs when the body’s healthy skin cells get attacked by the immune system causing inflammation, damage, and various skin symptoms. These disorders can not only affect the skin but are also believed harmful to other organs and systems in the body. It is important to understand these type of for timely diagnosis and treatment, as these conditions need long-term management to enhance the patient’s health.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for autoimmune skin disorders, and offer an depth study of how they are manifested and can managed effectively.
What Are Autoimmune Skin Disorders?
Autoimmune skin disorders occur when the immune system, which is designed to protect the body from infections and harmful invaders, malfunctions and begins to attack its tissues. In the case of skin-related autoimmune diseases, the immune response specifically targets skin cells, leading to chronic inflammation, rashes, blisters, or discoloration.
Examples of It include:
1. Psoriasis – Characterized by thick, scaly patches of skin.
2. Lupus – Often causes a butterfly-shaped rash on the face.
3. Vitiligo – This leads to loss of pigmentation in certain areas of the skin.
4. Bullous Pemphigoid – Results in large, fluid-filled blisters.
5. Dermatomyositis – Affects both the skin and muscles, causing rashes and muscle weakness.
Each of these disorders has unique features but shares the commonality of being triggered by an autoimmune reaction.
Causes of Autoimmune Skin Disorders
The exact causes of these skin disorders remain unclear. However, several factors are believed to contribute to their development:
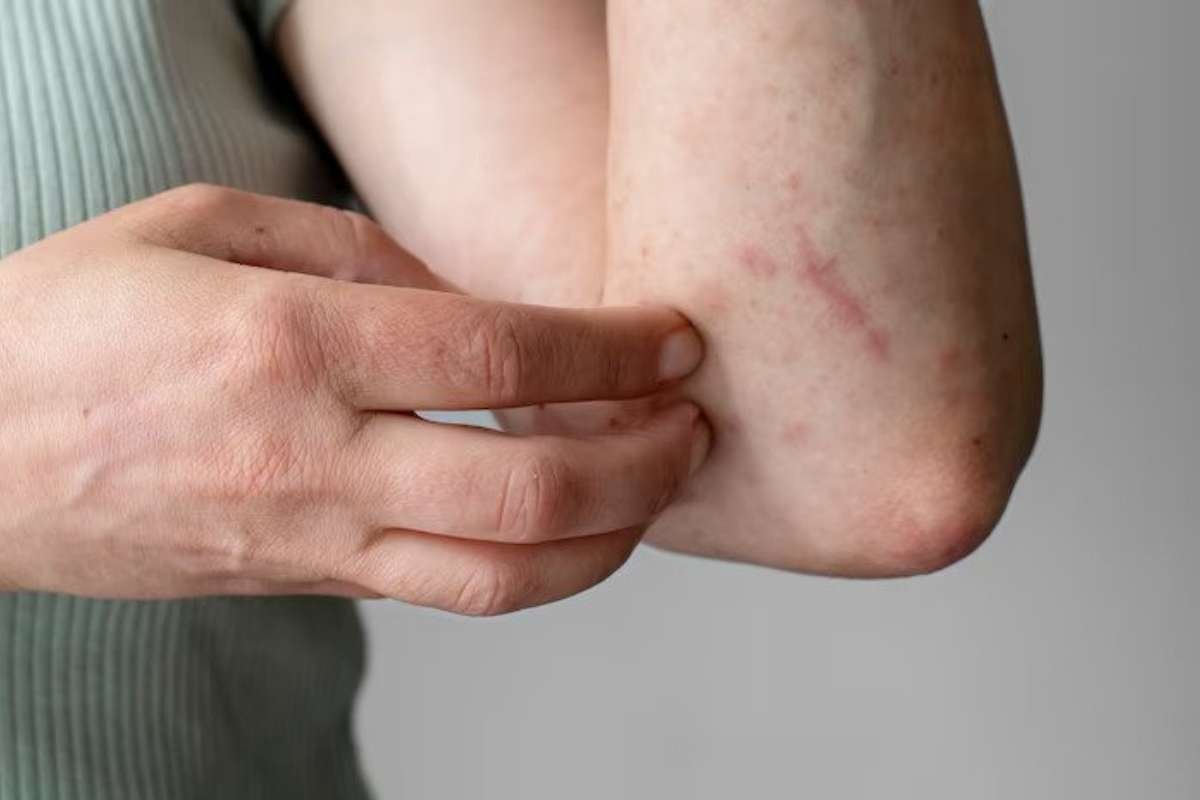
1. Genetics – A family history of autoimmune diseases increases the likelihood of developing one.
2. Environmental Triggers – Factors such as UV radiation, infections, stress, or exposure to certain chemicals may act as triggers.
3. Hormonal Imbalances – Hormonal changes can sometimes exacerbate autoimmune reactions.
4. Other Autoimmune Conditions – Individuals with one autoimmune disorder are more likely to develop another.
While these factors may predispose someone to autoimmune skin disorders, the interplay between genetics and environmental triggers is complex and not entirely understood.
Symptoms of these type of skin disorders
The symptoms of these type of skin disorders vary depending on the specific condition but may include:
1. Rashes – These can appear as red, scaly, or itchy patches.
2. Blisters – Fluid-filled blisters are common in conditions like bullous pemphigoid.
3. Pigmentation Changes – Vitiligo causes depigmented or white patches on the skin.
4. Thickened Skin – Psoriasis often leads to thick, scaly skin plaques.
5. Ulcers or Lesions – Chronic sores or ulcers may develop in certain cases.
Symptoms may range from mild and localized to severe and widespread. They can also flare up and subside intermittently, making the condition unpredictable.
Diagnosing Autoimmune Skin Disorders
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for managing autoimmune skin disorders effectively. Dermatologists typically use the following methods:
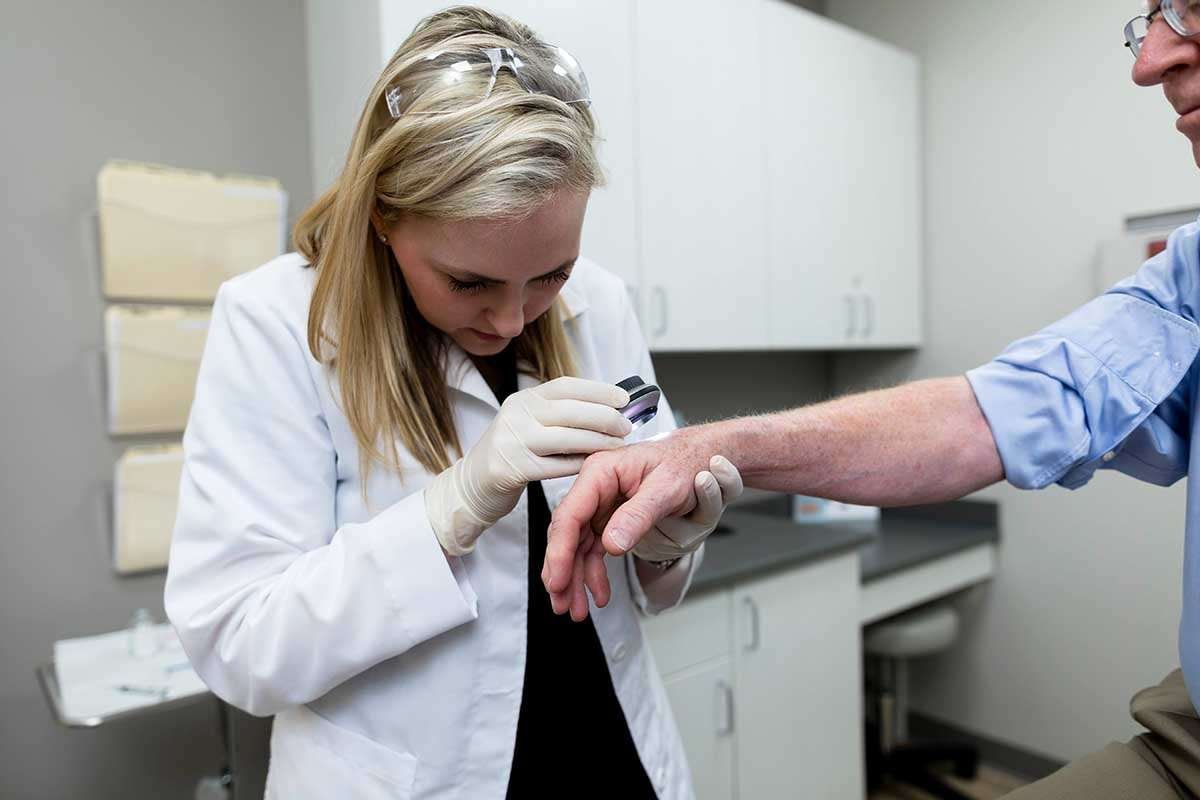
1. Clinical Examination – Observing the appearance and distribution of skin symptoms.
2. Biopsy – A small sample of skin tissue is examined under a microscope to identify specific markers of autoimmune activity.
3. Blood Tests – These tests check for the presence of autoantibodies that indicate an autoimmune response.
Timely diagnosis helps in formulating an effective treatment plan to prevent further complications.
Treatment Options for Autoimmune Skin Disorders
Managing these type of skin disorders involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes alternative therapies. The goal is to reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and improve the overall quality of life.
1. Medications
- Topical Treatments: Creams or ointments containing corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, or retinoids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms.
- Systemic Medications: In more severe cases, drugs like methotrexate, cyclosporine, or biologics are used to suppress the immune system.
- Antimalarials: Medications like hydroxychloroquine are effective for lupus-related skin symptoms.
2. Lifestyle Modifications

- Healthy Diet: An anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce symptoms.
- Stress Management: Stress is a known trigger for autoimmune flares, so practices like yoga, meditation, or mindfulness are beneficial.
- Sun Protection: UV rays can worsen conditions like lupus, so wearing sunscreen and protective clothing is essential.
3. Alternative Therapies
Some patients find relief in alternative treatments such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, or light therapy (phototherapy). However, these should be pursued only under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Living with Autoimmune Skin Disorders
Living with autoimmune skin disorders can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. The visible nature of these conditions often affects a person’s self-esteem and mental health. Joining support groups, seeking therapy, or consulting a counselor can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of the disease.
Additionally, maintaining regular check-ups with a dermatologist and following the prescribed treatment plan can significantly improve outcomes. Education about the condition also empowers patients to take control of their health.
Advancements in Research
Ongoing research into autoimmune skin disorders is providing hope for better treatments and potential cures. Scientists are exploring the genetic basis of these disorders, identifying new biomarkers for early detection, and developing innovative therapies that target the immune system more precisely.
Biologic drugs, in particular, have revolutionized the treatment landscape by targeting specific immune pathways, offering patients relief from symptoms with fewer side effects compared to traditional treatments.
Conclusion
Autoimmune skin disorders cover a vast range of conditions that result from the immune system attacking healthy skin cells. Though the actual causes of this are still unclear, the genetic Comprehensive and environmental triggers play a vital role. The key to managing these conditions effectively is early diagnosis and Comprehensive treatment.
By studying the It, and the treatment options available, patients can cooperate with healthcare providers to build a personalized management plan. As research is also evolving, there is still a chance for creating effective therapies in the coming future to make sure every individual having this disease could live a long and healthier life.
These type of skin diseases could lead to lifelong challenges, however, with the right support, information, and medical treatment those affected can regain control and ehanching their quality of life.