Knee hyperextension is a common condition that affects many individuals, particularly athletes. This condition occurs when the knee joint is bent backward beyond its normal range of motion, which can lead to various degrees of injury. Understanding knee hyperextension is crucial for preventing and managing this injury effectively. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies for knee hyperextension.
What is Knee Hyperextension?
This occurs when the knee joint is forced to extend beyond its normal range of motion. This can happen due to various factors, including trauma, sports activities, or accidents. When the knee is hyperextended, the ligaments, tendons, and other soft tissues surrounding the joint can be damaged, leading to pain, swelling, and instability.
Causes of Knee Hyperextension
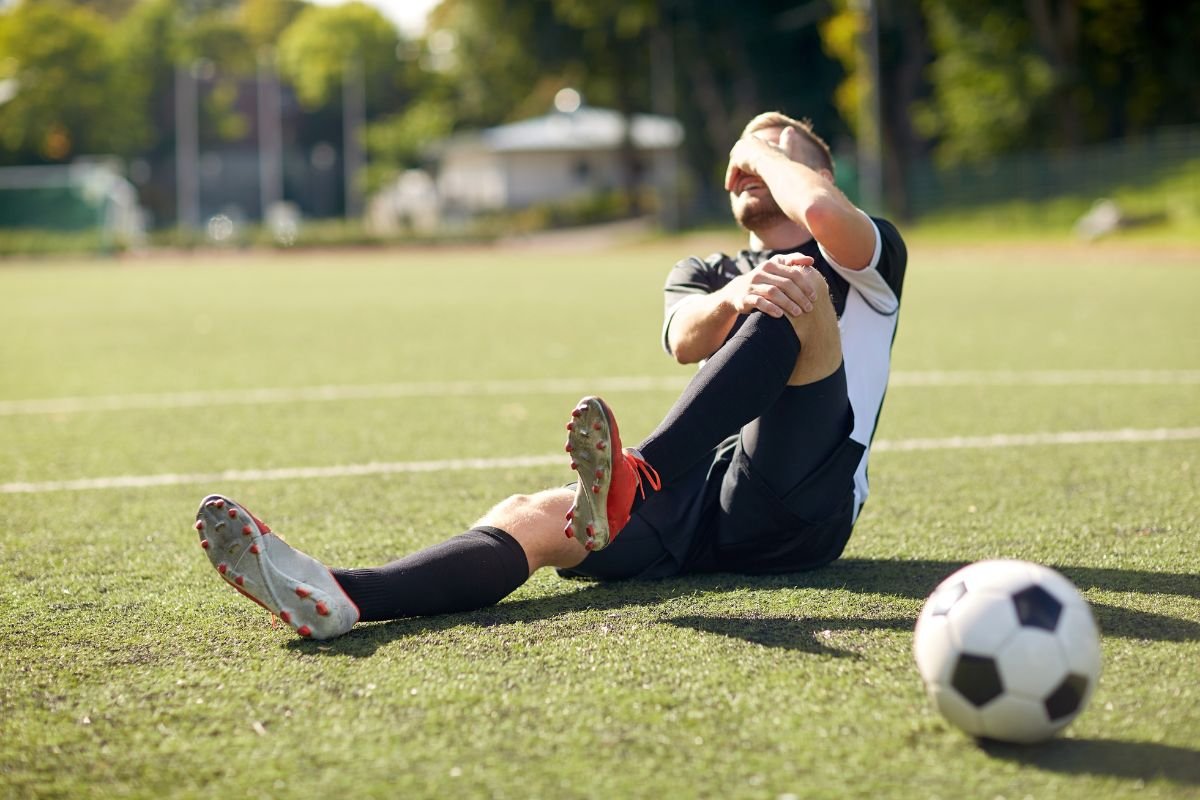

1. Sports Injuries
Athletes are particularly susceptible to knee hyperextension due to the high-impact and dynamic movements involved in sports. Activities such as basketball, soccer, gymnastics, and skiing can place excessive stress on the knee joint, increasing the risk of hyperextension.
2. Accidents
Accidental falls or collisions can force the knee joint beyond its normal range of motion, resulting in hyperextension. Car accidents, slips, and falls are common scenarios where this may occur.
3. Weak Muscles
Weakness in the muscles surrounding the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings, can contribute to knee hyperextension. When these muscles are not strong enough to support the joint, it becomes more vulnerable to injury.
4. Improper Training Techniques
Improper training techniques or inadequate warm-up and stretching routines can increase the risk of this. It is essential to use proper form and technique during physical activities to minimize the chances of injury.
Symptoms of Knee Hyperextension
The symptoms of knee hyperextension can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
1. Pain
Pain is one of the most common symptoms of knee hyperextension. The pain may range from mild to severe and is typically felt in the front or back of the knee joint.
2. Swelling
Swelling around the knee joint is another common symptom. This swelling is caused by inflammation and fluid buildup in the affected area.
3. Instability
Knee hyperextension can lead to a feeling of instability or giving way in the knee. This instability occurs due to the damage to the ligaments and other soft tissues that support the joint.
4. Bruising
Bruising may occur around the knee joint due to the trauma and damage to blood vessels caused by hyperextension.
5. Limited Range of Motion
Individuals with this may experience a limited range of motion in the affected knee. This can make it difficult to perform everyday activities such as walking, running, or climbing stairs.
Diagnosis of Knee Hyperextension
If you suspect you have knee hyperextension, it is essential to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis. A healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination and may order imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans to assess the extent of the injury. These tests can help determine the severity of the damage and guide the appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options
The treatment for this depends on the severity of the injury. Mild cases may be managed with conservative treatments, while severe cases may require surgical intervention. Here are some common treatment options:
1. Rest and Ice
Resting the affected knee and applying ice packs can help reduce pain and swelling. It is essential to avoid activities that exacerbate the injury and allow the knee to heal.
2. Compression and Elevation
Using compression bandages and elevating the leg can help reduce swelling and promote healing. These measures can also provide support to the injured knee.
3. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a crucial component of the rehabilitation process for knee hyperextension. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve joint stability.
4. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications if necessary.
5. Bracing
Wearing a knee brace can provide additional support and stability to the injured knee. Braces are particularly useful during physical activities to prevent further hyperextension.
6. Surgery
Severe cases of knee hyperextension that involve significant ligament or tendon damage may require surgical intervention. Surgery aims to repair the damaged structures and restore the normal function of the knee joint.
Prevention of Knee Hyperextension

Preventing this is essential, especially for individuals who are active in sports or other physical activities. Here are some tips to help prevent knee hyperextension:
1. Strengthening Exercises
Regularly performing exercises that strengthen the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings, can provide better support to the joint and reduce the risk of hyperextension.
2. Proper Warm-Up
Always warm up before engaging in physical activities. A proper warm-up routine increases blood flow to the muscles and prepares them for the demands of exercise.
3. Use Proper Techniques
Using correct techniques and form during sports and exercise can minimize the risk of knee hyperextension. Avoiding sudden, jerky movements and practicing controlled motions can help protect the knee joint.
4. Wear Appropriate Footwear
Wearing appropriate footwear that provides adequate support and cushioning can help reduce the impact on the knee joint and lower the risk of hyperextension.
5. Balance Training
Incorporating balance training exercises into your routine can improve proprioception and enhance the stability of the knee joint, reducing the likelihood of hyperextension injuries.
6. Avoid Overtraining
Avoid overtraining and allow sufficient time for rest and recovery between workouts. Overuse and fatigue can increase the risk of knee injuries, including hyperextension.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of knee hyperextension, especially if the pain is severe or persistent. Delaying treatment can lead to further damage and complications. If you notice any of the following symptoms, consult a healthcare professional:
- Severe pain that does not improve with rest and ice
- Significant swelling around the knee joint
- A feeling of instability or the knee giving way
- Inability to bear weight on the affected leg
- Visible deformity or abnormal positioning of the knee
Conclusion
Knee hyperextension is a common injury that can affect individuals of all ages, particularly those involved in sports and physical activities. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and prevention. By taking proactive measures such as strengthening exercises, proper warm-up routines, and correct techniques, you can reduce the risk of knee hyperextension and maintain healthy knee joints. If you experience symptoms of knee hyperextension, seek medical attention promptly to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. With the right care and precautions, you can recover from knee hyperextension and continue to enjoy an active lifestyle.