In the realm of healthcare, the field of Anatomic Pathology plays a pivotal role in diagnosing diseases, guiding treatment decisions, and advancing medical research. With its focus on examining tissues and cells at a microscopic level, Anatomic Pathology provides invaluable insights into the underlying mechanisms of disease and informs personalized patient care. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the intricacies of Anatomic Pathology, its applications across various medical specialties, and the evolving landscape of diagnostic techniques and technologies.
Understanding Anatomic Pathology
Anatomic Pathology, also referred to as anatomical pathology or histopathology, encompasses the study of tissue specimens obtained from surgical procedures, biopsies, or autopsies. It involves the microscopic examination of tissues and cells to identify abnormalities, characterize diseases, and provide diagnostic insights to clinicians. Through the interpretation of tissue morphology, cellular architecture, and molecular markers, Anatomic Pathologists play a crucial role in diagnosing a wide range of conditions, from common diseases to rare malignancies.
Anatomic Pathology is a cornerstone of modern medicine, providing vital information that guides clinical decision-making and patient management. Utilizing advanced laboratory techniques and diagnostic tools, Anatomic Pathologists meticulously analyze tissue samples to identify structural changes, cellular abnormalities, and disease processes. This comprehensive approach not only aids in diagnosing diseases but also facilitates prognostication, treatment planning, and therapeutic monitoring.
In addition to its diagnostic role, Anatomic Pathology contributes to medical research, education, and quality assurance initiatives. By studying tissue specimens under the microscope and employing ancillary testing methods such as immunohistochemistry, molecular genetics, and cytogenetics, pathologists gain valuable insights into disease mechanisms, genetic alterations, and therapeutic targets. Furthermore, Anatomic Pathologists collaborate with multidisciplinary teams of clinicians, surgeons, radiologists, and laboratory professionals to ensure accurate diagnosis and optimal patient care.
Applications Across Medical Specialties
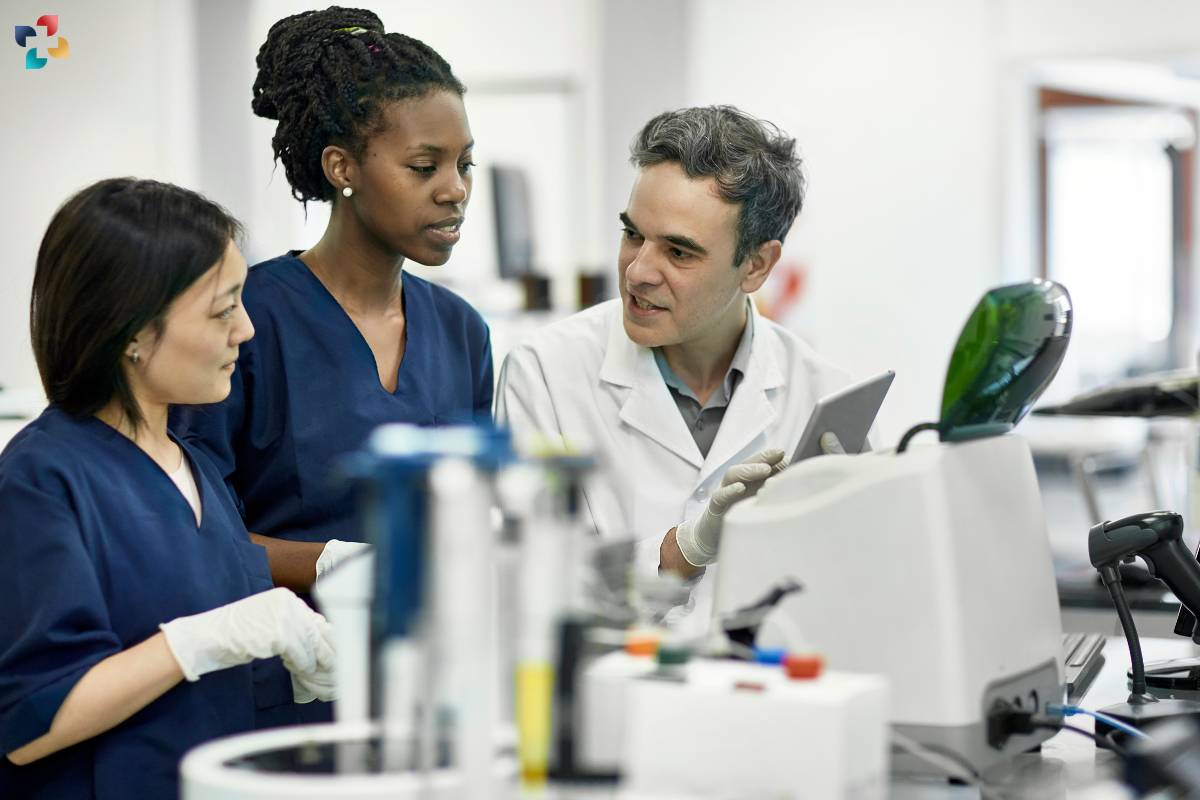

The utility of Anatomic Pathology extends across various medical specialties, each with its unique diagnostic challenges and requirements. In surgical pathology, Anatomic Pathologists analyze tissue specimens removed during surgeries to diagnose tumors, assess tumor margins, and determine the extent of disease spread. In dermatopathology, they specialize in diagnosing skin disorders and melanocytic lesions through the examination of skin biopsies and excisions. In cytopathology, they evaluate cellular samples obtained from body fluids or fine needle aspirates to diagnose conditions such as cancer, infections, and inflammatory diseases.
Diagnostic Techniques and Technologies
Advancements in diagnostic techniques and technologies have revolutionized the practice of Anatomic Pathology, enabling rapid and accurate diagnosis of complex diseases. Traditional histological techniques, such as hematoxylin and eosin staining, remain fundamental to tissue examination. However, innovative approaches, including immunohistochemistry, molecular pathology, and digital pathology, have expanded the diagnostic capabilities of Anatomic Pathologists. Immunohistochemistry allows for the detection of specific proteins within tissue specimens, aiding in the characterization of tumors and the identification of therapeutic targets.
Molecular pathology techniques, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and next-generation sequencing (NGS), enable the analysis of genetic mutations and molecular alterations associated with cancer and inherited diseases. Digital pathology platforms facilitate the digitization of glass slides, enabling remote viewing, image analysis, and collaborative consultations among pathologists.
Role in Personalized Medicine
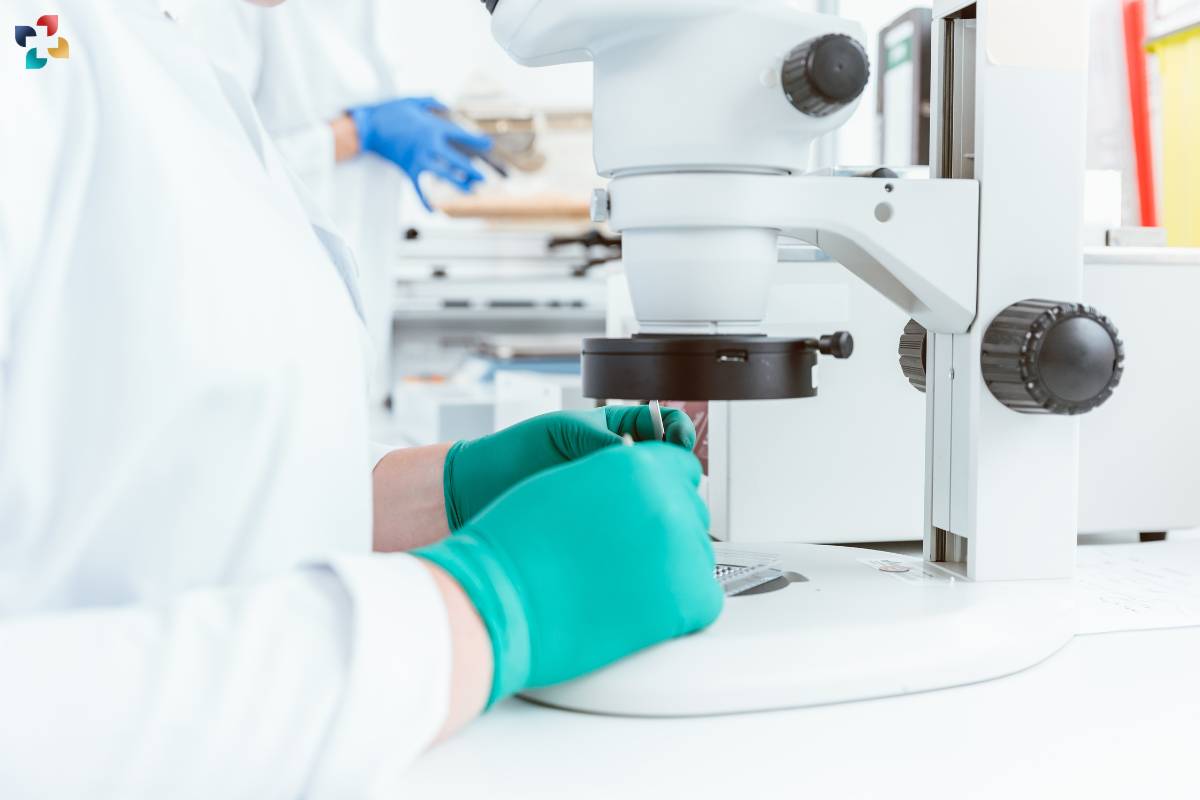

Anatomic Pathology plays a central role in the era of personalized medicine, where treatment decisions are tailored to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup, disease characteristics, and treatment response. By integrating molecular diagnostics and genomic profiling into routine practice, Anatomic Pathologists can identify actionable mutations, predict treatment outcomes, and guide targeted therapies. In oncology, molecular profiling of tumors informs the selection of targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and precision medicine approaches, optimizing treatment efficacy and minimizing adverse effects.
Moreover, Anatomic Pathologists contribute to the interpretation of biomarkers, prognostic indicators, and predictive factors that influence treatment decisions across various disease entities.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its indispensable role in healthcare, Anatomic Pathology faces several challenges, including workforce shortages, increasing workloads, and evolving regulatory requirements. The demand for timely and accurate diagnoses continues to grow, driven by an aging population, advances in diagnostic technologies, and the expanding scope of personalized medicine.
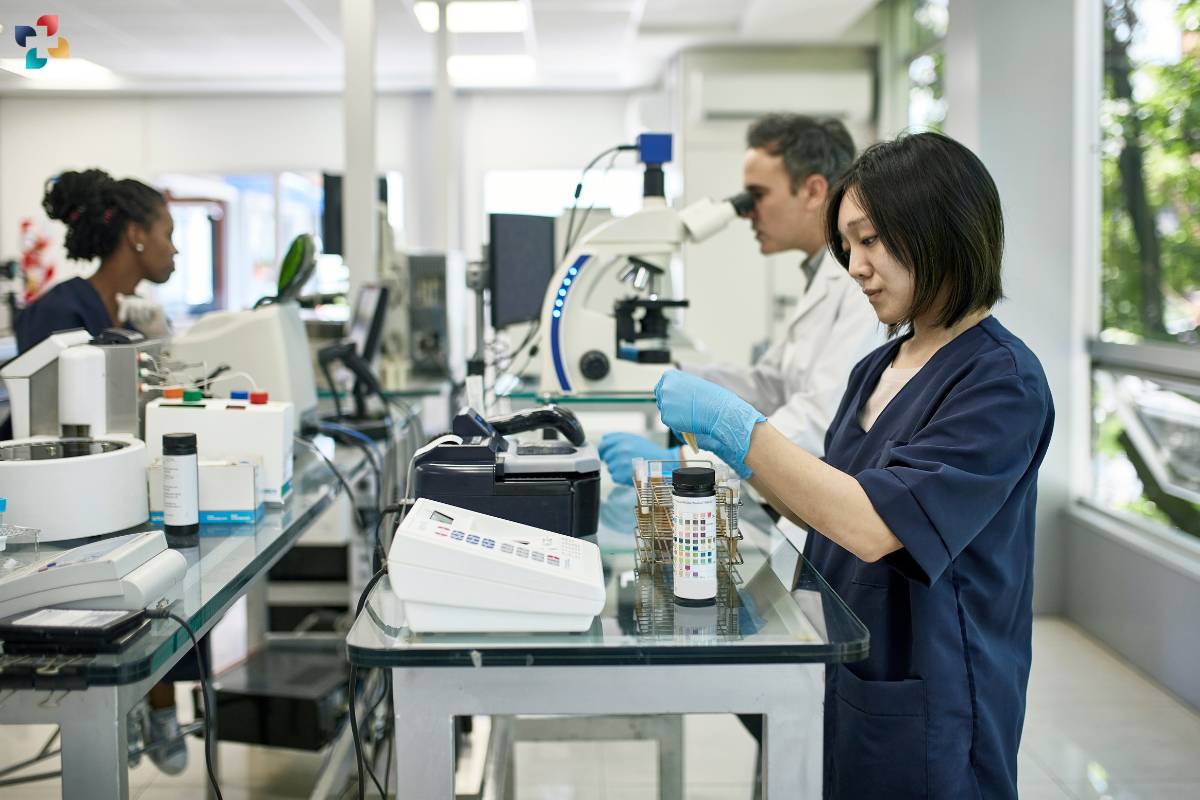

Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into Anatomic Pathology holds promise for enhancing diagnostic accuracy, workflow efficiency, and decision support. By leveraging AI-powered image analysis tools and computational algorithms, Anatomic Pathologists can streamline tissue interpretation, reduce diagnostic variability, and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Anatomic Pathology stands at the forefront of modern medicine, providing essential diagnostic insights that drive patient care, treatment decisions, and medical research. Through the microscopic examination of tissues and cells, Anatomic Pathologists unravel the complexities of disease pathology, contributing to early detection, accurate diagnosis, and targeted therapies.
With advancements in diagnostic techniques, molecular technologies, and personalized medicine approaches, Anatomic Pathology continues to evolve, offering new opportunities to improve patient outcomes and advance our understanding of human health and disease. As we navigate the complexities of healthcare delivery, Anatomic Pathology remains a cornerstone of medical practice, delivering invaluable insights that shape the future of medicine.
FAQs
1. What is Anatomic Pathology, and what does it entail?
Anatomic Pathology, also known as anatomical pathology or histopathology, involves the study of tissue specimens obtained from surgical procedures, biopsies, or autopsies. It encompasses the microscopic examination of tissues and cells to identify abnormalities, characterize diseases, and provide diagnostic insights to clinicians.
2. What types of specimens are analyzed in Anatomic Pathology?
Anatomic Pathologists analyze a wide range of tissue specimens, including surgical specimens, biopsies (such as needle biopsies or endoscopic biopsies), cytology samples (such as fine needle aspirates or Pap smears), and postmortem tissues obtained during autopsies.
3. What role do Anatomic Pathologists play in patient care?
Anatomic Pathologists play a crucial role in patient care by providing diagnostic interpretations of tissue specimens. Their findings aid clinicians in accurately diagnosing diseases, determining appropriate treatment strategies, assessing prognosis, and monitoring treatment response.
4. How are tissue specimens processed and analyzed in Anatomic Pathology?
Upon receipt of tissue specimens, Anatomic Pathologists process them through various laboratory techniques, including tissue fixation, embedding, sectioning, staining, and microscopic examination. Ancillary tests such as immunohistochemistry, molecular genetics, and cytogenetics may also be performed to further characterize diseases.
5. What is the difference between Anatomic Pathology and Clinical Pathology?
Anatomic Pathology primarily involves the examination of tissues and cells under the microscope to diagnose diseases based on their morphological features. In contrast, Clinical Pathology focuses on the analysis of bodily fluids (such as blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid) and other specimens (such as bone marrow aspirates and body fluids) to diagnose diseases using laboratory tests, including hematology, clinical chemistry, microbiology, and immunology.