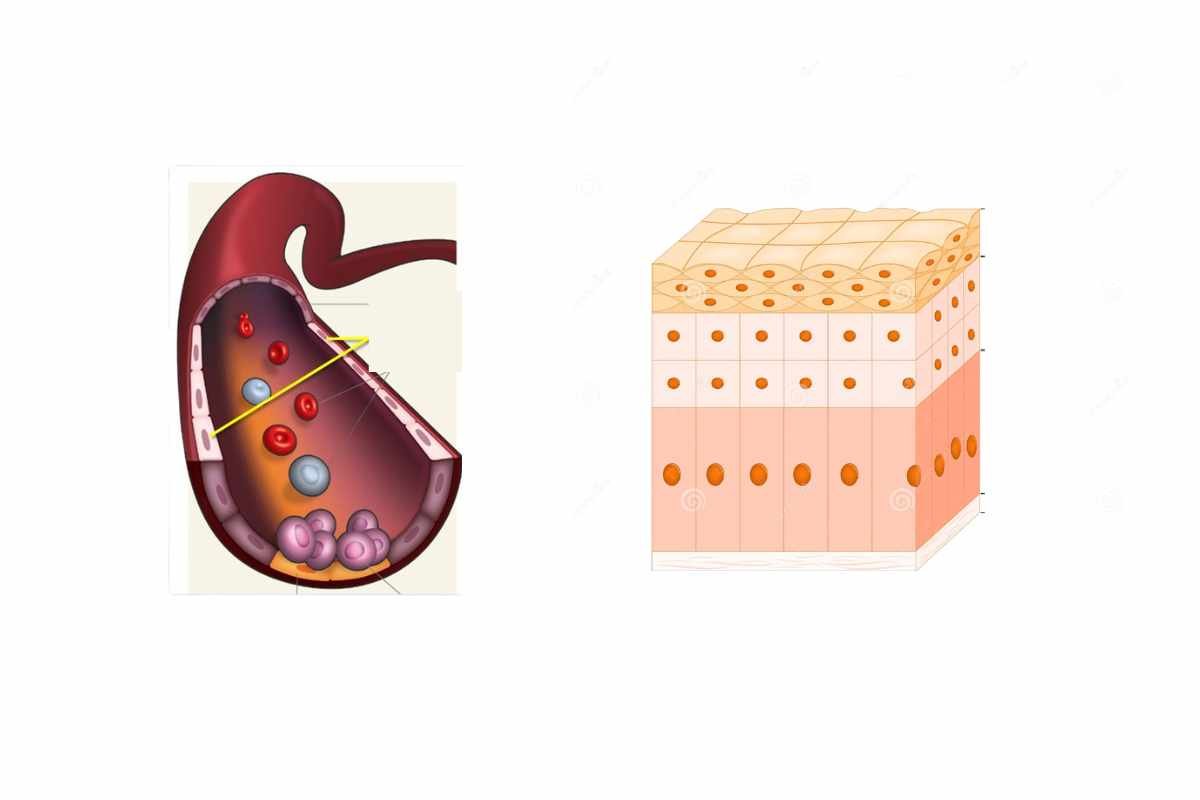
Our Body is made up of multiple cells that carry out various important functions in our body, such as providing structure to our body, taking in nutrients from food, and converting it into energy. Among these infinite numbers of cells, we have two special cells that carry out crucial functions in the human body. They are called endothelial cells and epithelial cells. It is not easy to distinguish between them, but with some distinct features with which you can identify them, we will get into a comparison of endothelial cells vs epithelial cells.
The Endothelial cells are the cells that cover the inner surface of the blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and the heart by forming a single layer of cells called endothelium. The epithelial cells cover the outer surface of the internal organs and our body. They build a protective barrier for your internal organs to be safe from the outside world. They both possess different functions and have stayed in various positions. These cells are fascinating with their structure, the way they function, and many more things.
In this article, we will delve deep into the world of these cells and understand their difference. And also provides an overview of endothelial cells vs epithelial cells and studies their roles in the human body.
What are Endothelial Cells and Epithelial Cells?
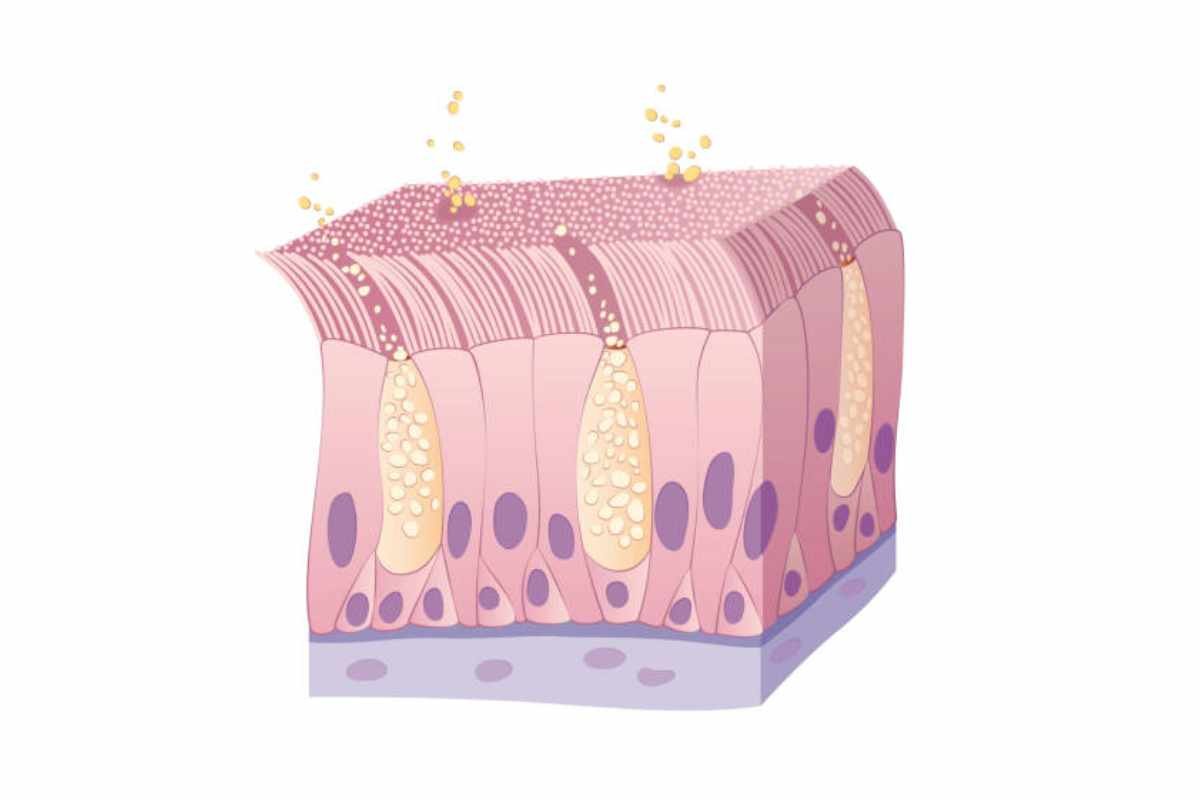
The Endothelial cells are also known as the unsung heroes of blood vessels. They are usually overlooked, but they play a vital role in maintaining the health and smooth functioning of our cardiovascular system. If there is any dysfunction or impaired function in these endothelial cells, it could lead to various cardiovascular diseases such as Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and diabetes. On the other hand, the epithelial cells are the protective shield of the human body. They are important for maintaining the health and functioning of our body. They offer a protective barrier and facilitate the absorption of nutrients while playing a vital role in many physiological processes.
Difference: Endothelial cells vs Epithelial cells.
Definition:
- Endothelial cells – they are the cells that cover the interior surface of the circulatory and lymphatic systems.
- Epithelial cells – these cells cover the outer surface of the organs and blood vessels and in surface of cavities.
Lining:
- Endothelial cells – they are known for lining only the inner surface of cavities.
- Epithelial cells – they usually line both the internal and the external surface of cavities.
Types:
- Endothelial cells – these cells are completely squamous.
- Epithelial cells – these cells can be squamous, cuboidal, or columnar.
Structures & number of cell layers:
- Endothelial cells – these cells include a single layer of squamous cells and the mono-layered structure allows water and oxygen molecules to pass through.
- Epithelial cells – these cells are tightly packed like bricks and may include single or multiple layers. They also have different types of structures which offer protection from the external environment.
Filaments:
- Endothelial cells – these cells are supported by vimentin filaments.
- Epithelial cells – these cell structures are supported by keratin filaments.
Surface layer:
- Endothelial cells – Endothelial cells have a smooth surface without any projections.
- Epithelial cells – Papillary projections may be visible on the surface of some epithelial cells.
Function of Endothelial cells vs Epithelial cells:
Endothelial Cells:
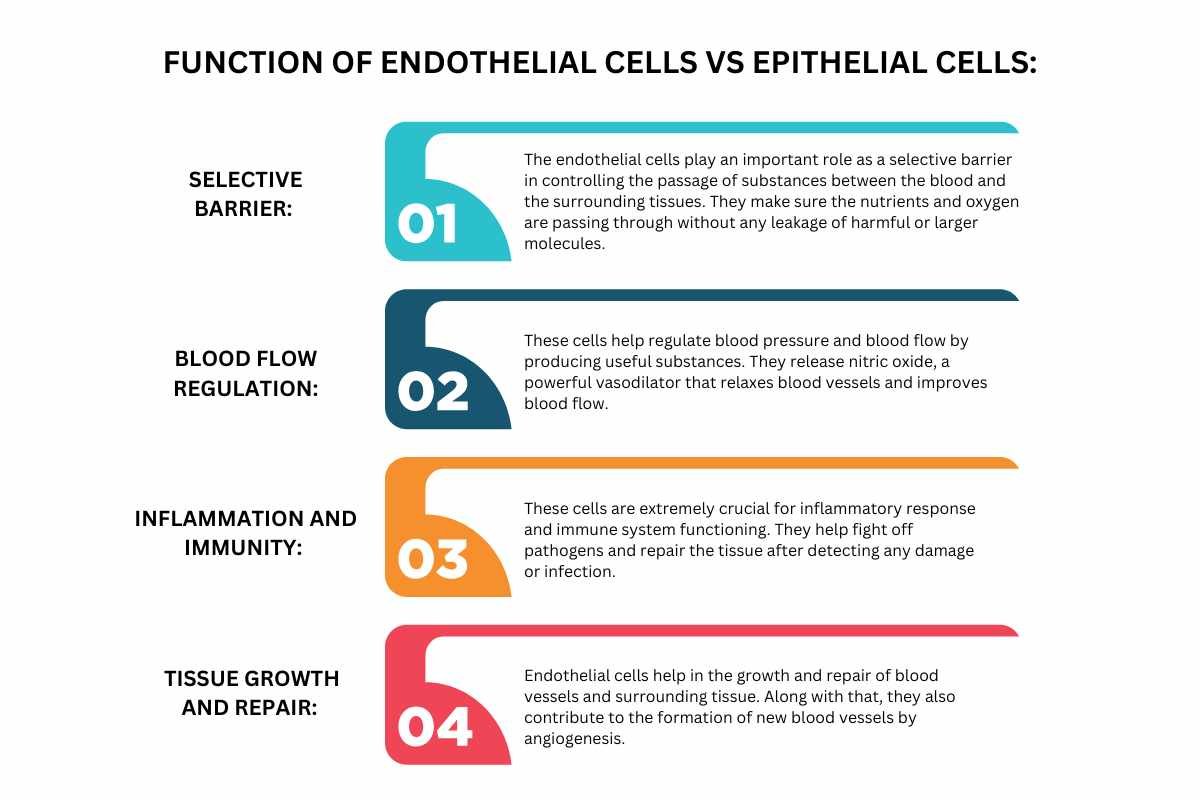
1. Selective barrier
The endothelial cells play an important role as a selective barrier in controlling the passage of substances between the blood and the surrounding tissues. They make sure the nutrients and oxygen are passing through without any leakage of harmful or larger molecules.
2. Blood flow regulation
These cells help regulate blood pressure and blood flow by producing useful substances. They release nitric oxide, a powerful vasodilator that relaxes blood vessels and improves blood flow.
3. Inflammation and immunity
These cells are extremely crucial for inflammatory response and immune system functioning. They help fight off pathogens and repair the tissue after detecting any damage or infection.
4. Tissue growth and repair
Endothelial cells help in the growth and repair of blood vessels and surrounding tissue. Along with that, they also contribute to the formation of new blood vessels by angiogenesis.
Epithelial Cells:
1. Protection
These form an important barrier for protection from any type of physical, chemical, and biological damage. They also act as a shield from injury, infections, and harmful substances.
2. Absorption
These cells play a vital role in absorbing the nutrients from food and other substances. Such as the epithelial cells lining your intestines absorb nutrients from digested food.
3. Secretion
These cells in glands secrete various substances, such as hormones, enzymes, and mucus.
4. Sensation
Some of these cells consist of sensory receptors that let you feel the touch, pressure, and temperature.
Conclusion:
The battle of Endothelial Cells vs Epithelial Cells is not going to end so soon. However, these unique cells have a huge part in making sure that our body is functioning smoothly and it’s being maintained. These cells take care of our cardiovascular and physiological processes. And provide various diseases to hamper our body by providing a protective barrier from any harmful substance and infection.
The endothelial cells provide a safe passage of nutrients to pass through surrounding tissues, and they are found in the inner surface of blood vessels. Whereas the epithelial cells protect our body and organs from any injury, infections, and damage.
This concept of endothelial cells vs epithelial cells can concluded with the fact that both of them are essential parts of our cell system. Without their existence, our body could be hamper from various harmful diseases.
How is epithelium different from endothelium vs epidermis?
Epithelial cells vary in function and adapt to the part of the body they are in. Endothelial cells are a specialized type of epithelium. While the endothelium only covers internal areas of the body, the epithelium also lines external tissues, such as the skin.
What are the endothelial cells in the eye?
The endothelium is a monolayer of cells on the posterior corneal surface that transports water from the stroma into the anterior chamber. This movement of water counters a natural tendency for the stroma to swell and is necessary to maintain a transparent cornea.
What are epithelial cells?
Epithelial cells cover the inside and outside of the surfaces of your body. They are found on your skin, blood vessels, and organs, including your urinary tract (which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra).