Table of Contents
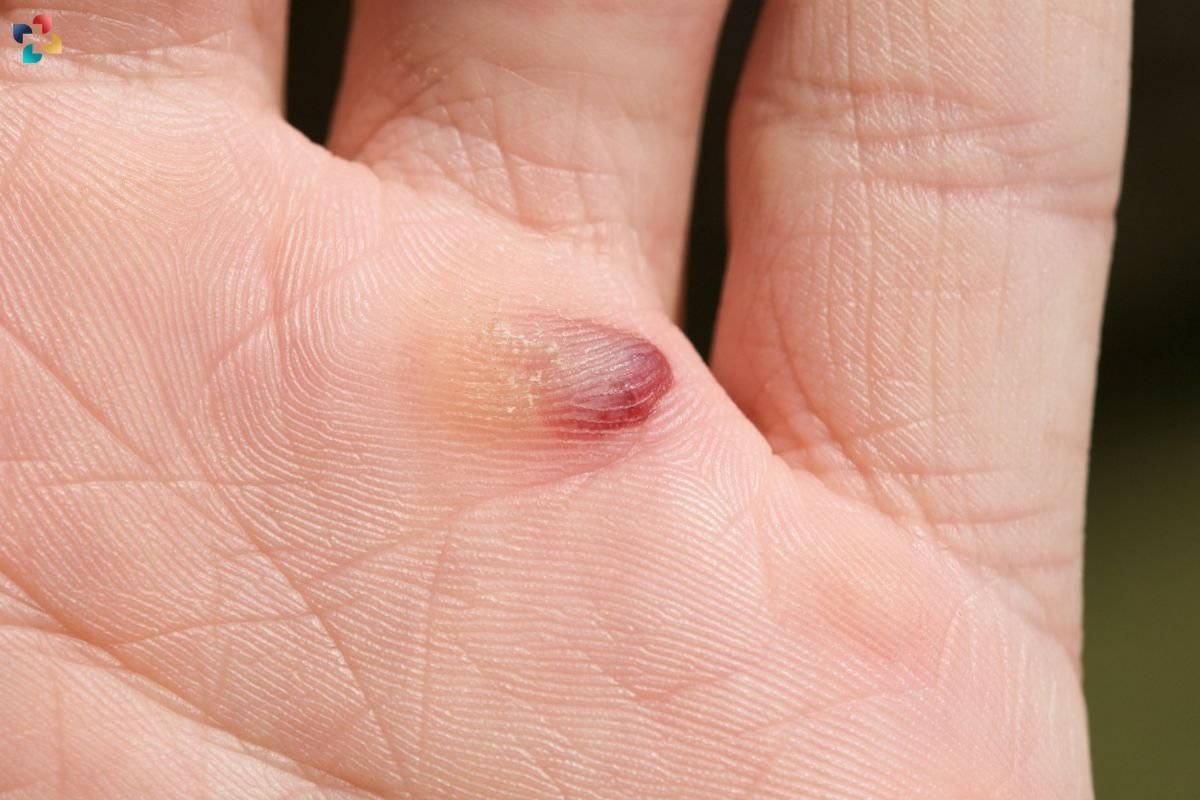
Blood blisters are a common yet often misunderstood skin condition. Unlike regular blisters filled with clear fluid, blood blisters are filled with blood, giving them a reddish or purplish appearance. While they can occur on any part of the body, they are most frequently found on areas subjected to pressure or friction, such as the hands and feet. This article will explore the causes, treatment options, and preventive measures for blood blisters, providing a comprehensive understanding of this skin condition.
What Are Blood Blisters?
Blood blisters are a type of blister that forms when blood vessels near the surface of the skin are damaged without the skin being broken. This damage causes blood to leak into the blister, resulting in a raised, fluid-filled bump that is usually red or purple. They are generally harmless and heal on their own, but they can be painful and may sometimes require medical attention if they become infected or do not heal properly.
Causes of Blood Blisters
Blood blisters are typically caused by trauma or injury to the skin. Some common causes include:
- Friction and Pressure: Repeated friction or pressure on the skin can damage the blood vessels underneath, leading to blood blisters. This is common in activities such as running, walking in ill-fitting shoes, or handling tools without gloves.
- Pinching: Accidentally pinching the skin, especially in areas where the skin is thin and the blood vessels are close to the surface, can cause blood blisters. Examples include catching a finger in a door or pinching skin in machinery.
- Burns: Thermal or chemical burns can damage the blood vessels and cause blood blisters to form.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hemophilia or other bleeding disorders, can make individuals more prone to developing blood blisters.
Symptoms of Blood Blisters
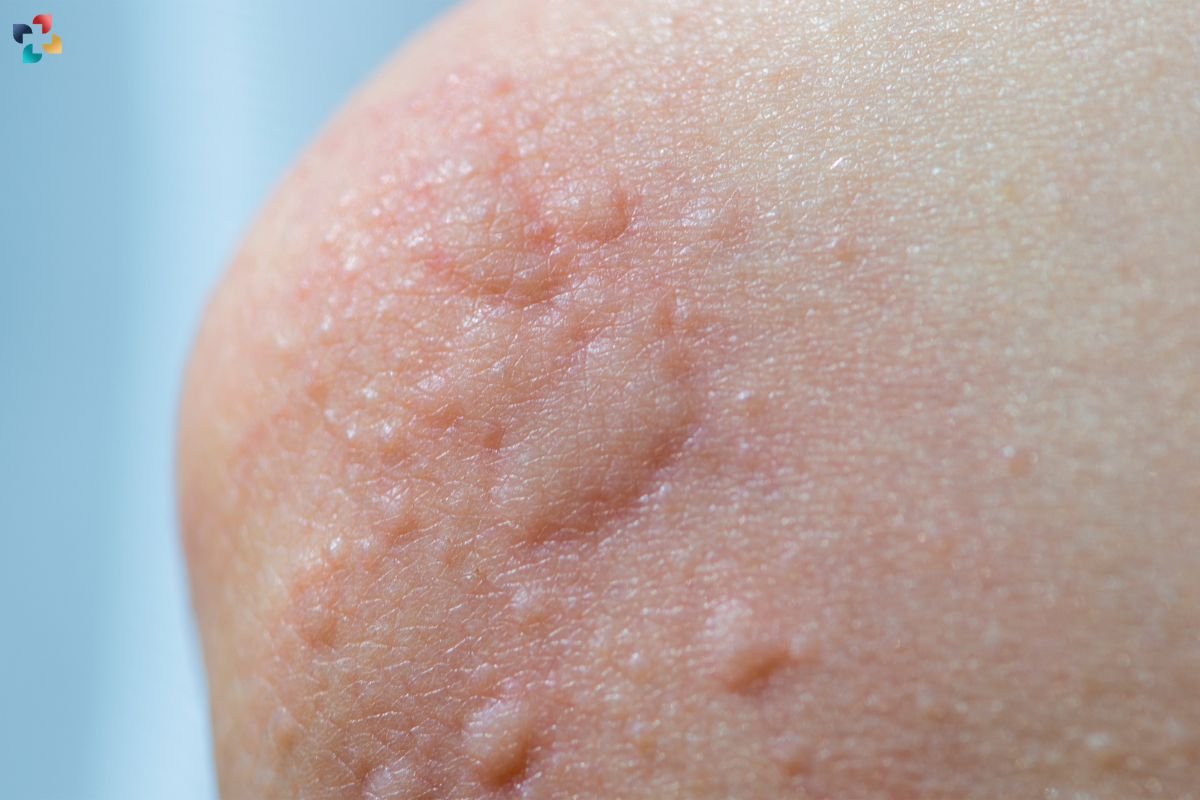
The primary symptom of a blood blister is a raised, fluid-filled bump on the skin that is red or purple in color. Other symptoms may include:
- Pain: Blood blisters can be painful, especially if they are in an area that is frequently used or subjected to pressure.
- Swelling: The area around the blister may be swollen.
- Tenderness: The skin around the blister may be tender to the touch.
Treatment for Blood Blisters
Most blood blisters heal on their own without the need for medical intervention. However, there are steps you can take to alleviate pain and prevent complications:
- Do Not Pop the Blister: Popping a blood blister can increase the risk of infection. It is best to let the blister heal naturally.
- Protect the Blister: Cover the blister with a sterile bandage or dressing to protect it from further friction and pressure.
- Apply Ice: Applying ice to the blister can help reduce pain and swelling. Be sure to wrap the ice in a cloth to avoid direct contact with the skin.
- Elevate the Affected Area: Elevating the affected area can help reduce swelling.
- Keep the Area Clean: Gently clean the area around the blister with mild soap and water to prevent infection.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most blood blisters heal without complications, there are situations where medical attention may be necessary:
- Infection: Signs of infection include increased pain, redness, warmth, swelling, or pus coming from the blister.
- Persistent Pain: If the blister is extremely painful and does not improve with home treatment, seek medical advice.
- Underlying Conditions: Individuals with underlying medical conditions that affect blood clotting or circulation should consult a healthcare provider if they develop blood blisters.
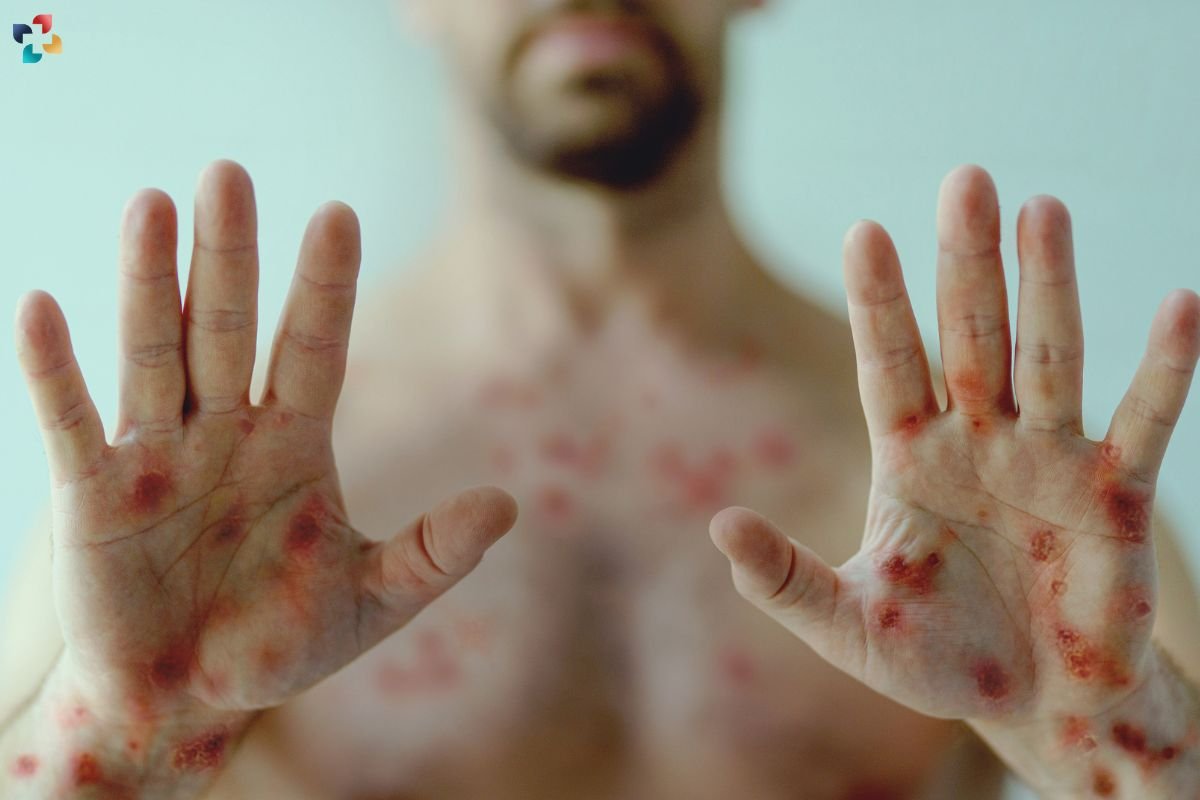

Prevention of Blood Blisters
Preventing blood blisters involves minimizing friction, pressure, and other forms of trauma to the skin. Here are some tips to help prevent it:
- Wear Proper Footwear: Ensure that shoes fit well and provide adequate support. Avoid wearing new shoes for extended periods until they are broken in.
- Use Protective Gear: Wear gloves when using tools or engaging in activities that may cause friction or pinching of the skin.
- Take Breaks: If you are engaged in an activity that involves repetitive motion or pressure, take regular breaks to reduce the risk of developing blood blisters.
- Use Padding: Apply padding or blister-resistant tape to areas of the skin that are prone to friction, such as the heels or palms.
- Stay Hydrated: Keeping the skin hydrated can help maintain its elasticity and reduce the risk of friction-related injuries.
Home Remedies for Blood Blisters
While blood blisters typically heal on their own, certain home remedies can help speed up the healing process and alleviate discomfort:
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce pain and swelling. Apply aloe vera gel directly to the blister.
- Witch Hazel: Witch hazel has astringent properties that can help dry out the blister and reduce swelling. Apply it to the blister using a cotton ball.
- Epsom Salt Soak: Soaking the affected area in an Epsom salt solution can help reduce swelling and promote healing. Mix two tablespoons of Epsom salt in a bowl of warm water and soak the blister for 15-20 minutes.
- Tea Tree Oil: Tea tree oil has antiseptic properties that can help prevent infection. Dilute a few drops of tea tree oil in a carrier oil and apply it to the blister.
- Turmeric Paste: Turmeric has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. Make a paste using turmeric powder and water, and apply it to the blister.
Understanding the Healing Process
The healing process of a blood blister involves several stages:
- Formation: The blister forms as blood leaks into the space between the skin layers due to damaged blood vessels.
- Protection: The body creates a protective layer over the blister to prevent further injury and infection.
- Reabsorption: The blood within the blister is gradually reabsorbed by the body.
- Healing: New skin forms beneath the blister, and the outer layer eventually dries up and peels off.
The entire healing process can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the size and location of the blood blister.
Complications of Blood Blisters
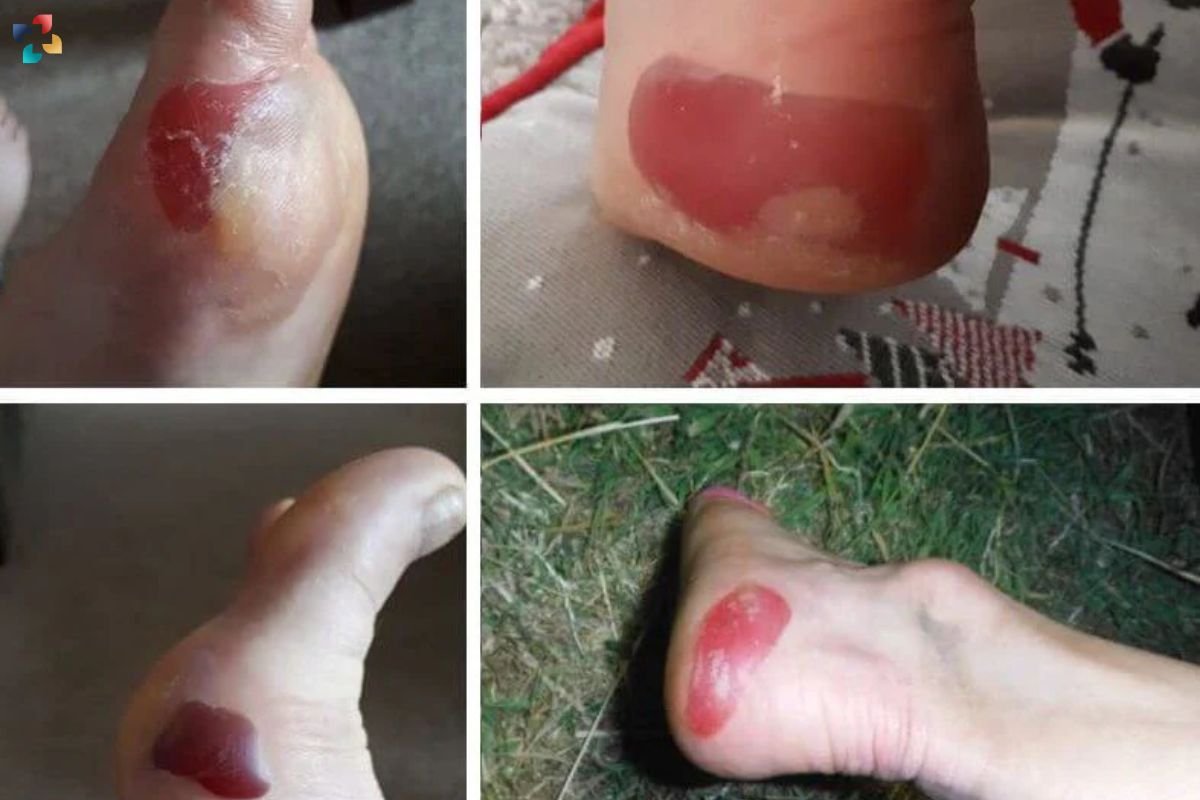
While blood blisters are generally benign, there are potential complications to be aware of:
- Infection: If a blood blister becomes infected, it can lead to more serious conditions, such as cellulitis or abscess formation. Signs of infection include increased redness, warmth, swelling, and the presence of pus.
- Scarring: In some cases, it may leave behind scars, especially if they are repeatedly irritated or if an infection occurs.
- Delayed Healing: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or poor circulation, can delay the healing of blood blisters.
Conclusion
Blood blisters, while often painful and alarming in appearance, are typically harmless and heal on their own with proper care. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals manage this condition effectively and prevent complications. By taking preventive measures, such as wearing proper footwear and using protective gear, you can reduce the risk of developing blood blisters. If a blood blister does occur, following home care tips and knowing when to seek medical attention can ensure a smooth and speedy recovery.
Whether you’re dealing with blood blisters from athletic activities, accidental pinches, or other forms of trauma, this guide provides the essential information needed to address and prevent it effectively. Remember, while most blood blisters are not serious, proper care and attention are key to maintaining healthy skin and preventing potential complications.
Demystifying Red Spots on Skin: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the various causes, symptoms, and treatment options for red spots on the skin, empowering readers to better understand and address this common dermatological concern.