The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has issued a travel alert warning about a chikungunya outbreak in southeast China, primarily affecting Guangdong province. The advisory, released on August 6, 2025, urges travelers to protect themselves from mosquito bites, as the virus is spreading rapidly in parts of the region.
Chikungunya is a mosquito-borne viral disease that can lead to significant discomfort and, in some cases, prolonged health effects. The CDC’s warning is part of its effort to reduce travel-related transmission and prevent further international spread.
Nearly 3,000 New Cases Reported in One Week
According to China’s National Health Commission, 2,940 new local cases of chikungunya were reported in Guangdong between July 20 and July 26, with most concentrated in the city of Foshan. While the cases were described as mild, authorities have emphasized the importance of prevention, as the virus is known to cause widespread discomfort and, in rare cases, long-term complications.
The World Health Organization (WHO) notes that chikungunya, first identified in Tanzania in 1952, has increasingly triggered outbreaks across Asia, Africa, Europe, and the Americas since 2004. In recent years, warming climates and growing urban populations have contributed to the wider spread of mosquito-borne diseases.
Symptoms, Risk Groups, and Preventive Measures
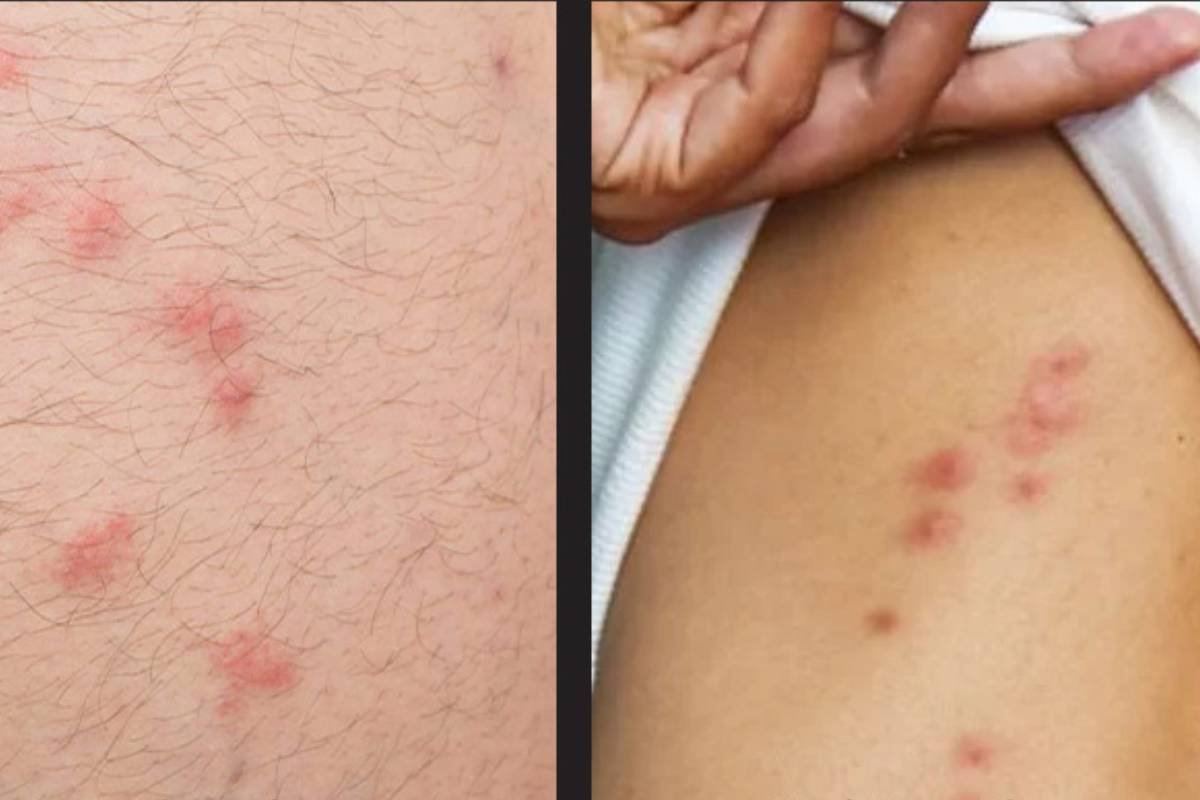
Chikungunya symptoms typically develop three to seven days after a bite from an infected mosquito. Common symptoms include fever, severe joint pain, headache, muscle pain, rash, and swelling. While most people recover within a week, joint pain can persist for months or even years in some cases.
The CDC highlighted that newborns, older adults, and individuals with pre-existing conditions such as heart disease or diabetes are more vulnerable to severe illness. Death from the virus remains rare, but health authorities stress the need for proactive protection.
Preventive steps include using insect repellent, wearing long-sleeved clothing, and minimizing outdoor exposure in mosquito-prone areas. Two vaccines approved in the United States are also recommended for travelers heading to regions experiencing outbreaks.
Economic and Travel Impact of the Outbreak
The Chikungunya Outbreak is expected to have short-term effects on Guangdong’s travel and tourism sector, as both domestic and international travelers respond to health warnings. Guangdong is one of China’s most visited provinces, with cities like Guangzhou and Shenzhen serving as key business and trade hubs.
Travel agencies have reported a rise in cancellations and inquiries about refunds for planned tours to the region. Local authorities are reassuring visitors that public health measures, such as mosquito control programs, are being expanded to minimize risk.
Economically, mosquito-borne outbreaks can lead to additional healthcare costs and reduced productivity as affected individuals take time off work to recover. Public health experts say that swift containment can limit the long-term impact on Guangdong’s economy, which is heavily reliant on manufacturing, trade, and tourism.
China Steps Up Efforts to Contain Spread
In response to the rising number of cases, China recently held a national conference focused on prevention and treatment strategies. Public health campaigns are underway in Guangdong to encourage community-wide mosquito control, including eliminating stagnant water sources where mosquitoes breed.
Authorities in both China and the United States continue to monitor the Chikungunya Outbreak closely. The CDC advises travelers planning visits to Guangdong or nearby regions to check updated alerts before departure and follow all recommended health precautions.
Source: