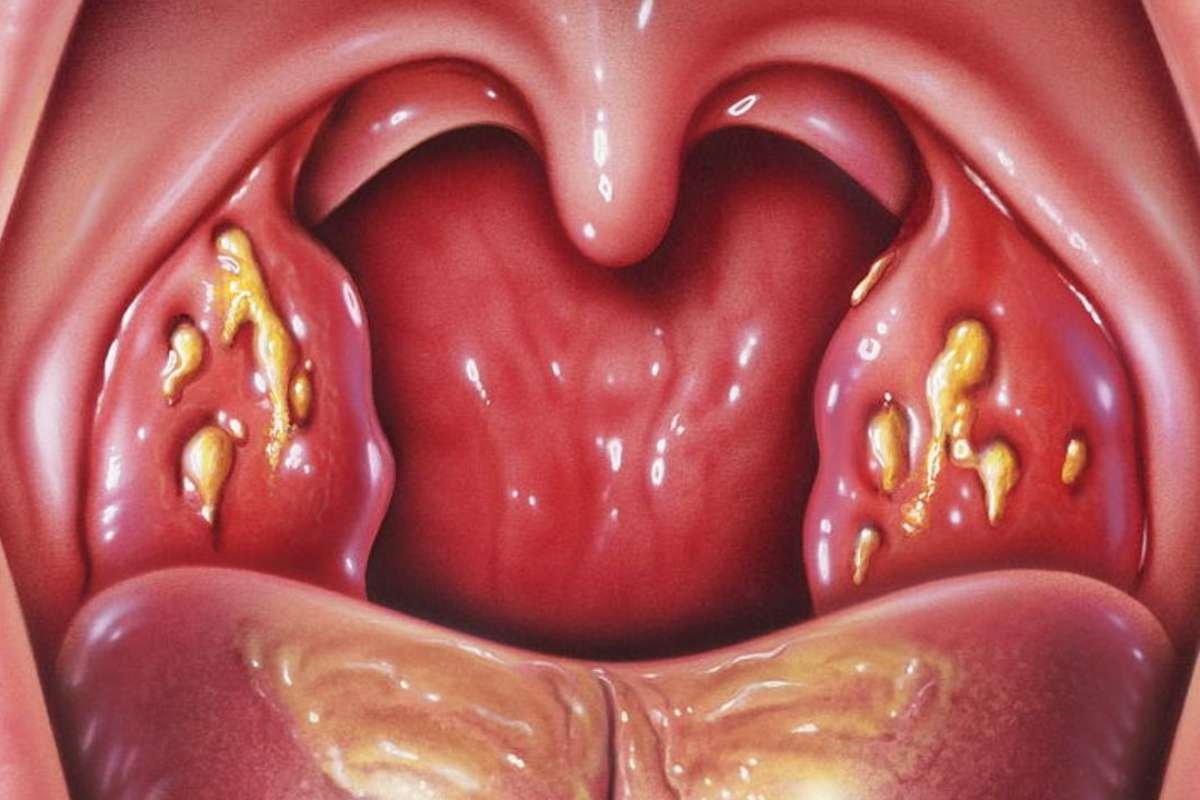
Seeing white spots on your tonsils can be worrying, especially if they show up suddenly or come with a sore throat and fever. Most of the time, these spots are not serious and can be treated easily, but sometimes they may mean a more serious problem. Knowing what causes these spots, how they look, and when to see a doctor is important for proper care and peace of mind.
In this guide, we will explain what white spots on tonsils might mean, possible causes, common signs, and treatment options from doctors.
What Are White Spots on Tonsils?
White spots on tonsils are usually patches of pus or debris that appear as white, yellowish, or grayish dots or coating on the surface of the tonsils. These spots are often signs of an infection or inflammation, but can also result from other health conditions. They may be isolated or widespread, and they can affect one or both tonsils.
Common Causes of White Spots on Tonsils
Several conditions can cause white spots to form on your tonsils. Here are the most common:
1. Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is the inflammation of the tonsils caused by viral or bacterial infections. When the tonsils become inflamed, they can develop white patches, especially in cases of bacterial tonsillitis, like strep throat.
Symptoms:
- Sore throat
- Swollen, red tonsils
- White or yellow spots
- Fever
- Difficulty swallowing
2. Strep Throat
Caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, strep throat is a highly contagious bacterial infection that often results in white spots on tonsils. It’s more common in children but can affect adults as well.
Symptoms:
- Severe sore throat
- Pain when swallowing
- Fever over 101°F (38.3°C)
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Absence of cough (a distinguishing feature)
Medical Insight: According to the CDC, strep throat accounts for approximately 15%-30% of sore throats in children and 5%-15% in adults. Source: CDC
3. Mononucleosis (Mono)
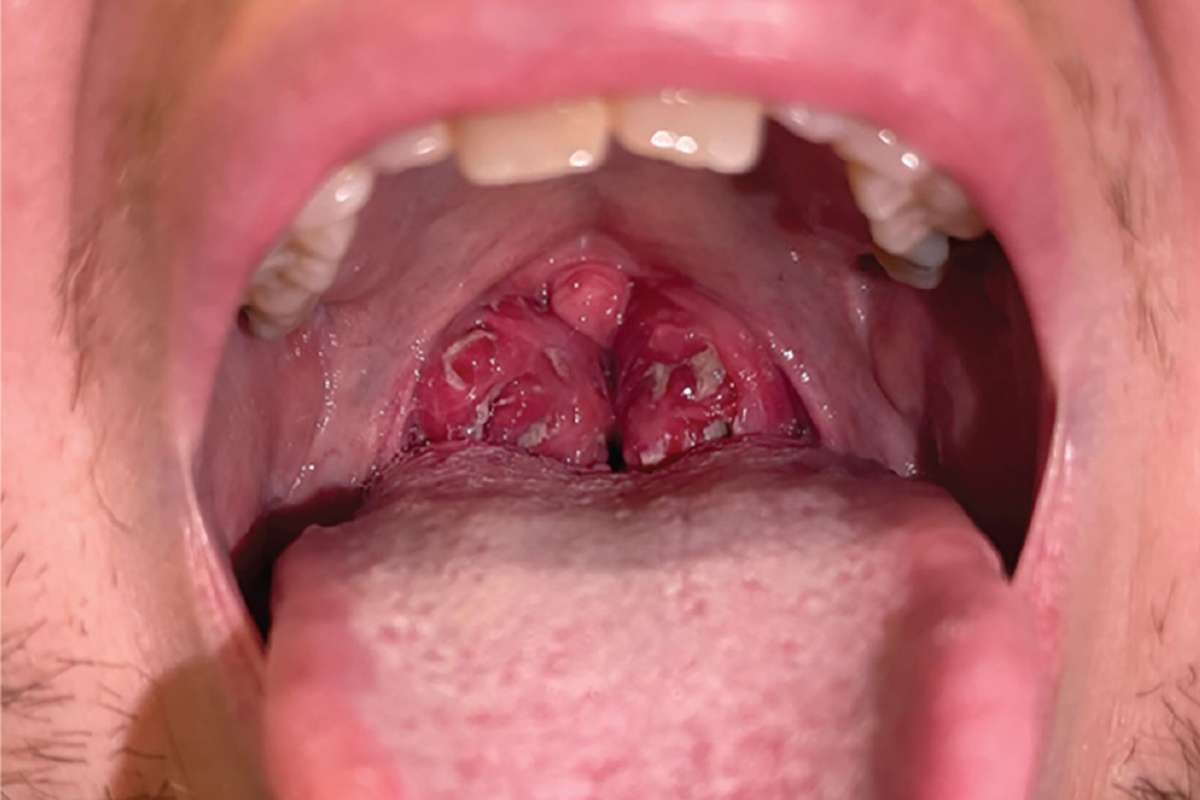
Often referred to as the “kissing disease,” mono is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. It can lead to large white patches on the tonsils and extreme fatigue.
Symptoms:
- Swollen tonsils with white coating
- Extreme tiredness
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
- Sore throat
4. Tonsil Stones (Tonsilloliths)
Tonsil stones are hardened calcium deposits that form in the crevices of the tonsils. These can appear as white or yellowish spots and may have an unpleasant odor.
Symptoms:
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Feeling of something stuck in your throat
- White, hard stones in the tonsils
- Difficulty swallowing
5. Oral Thrush
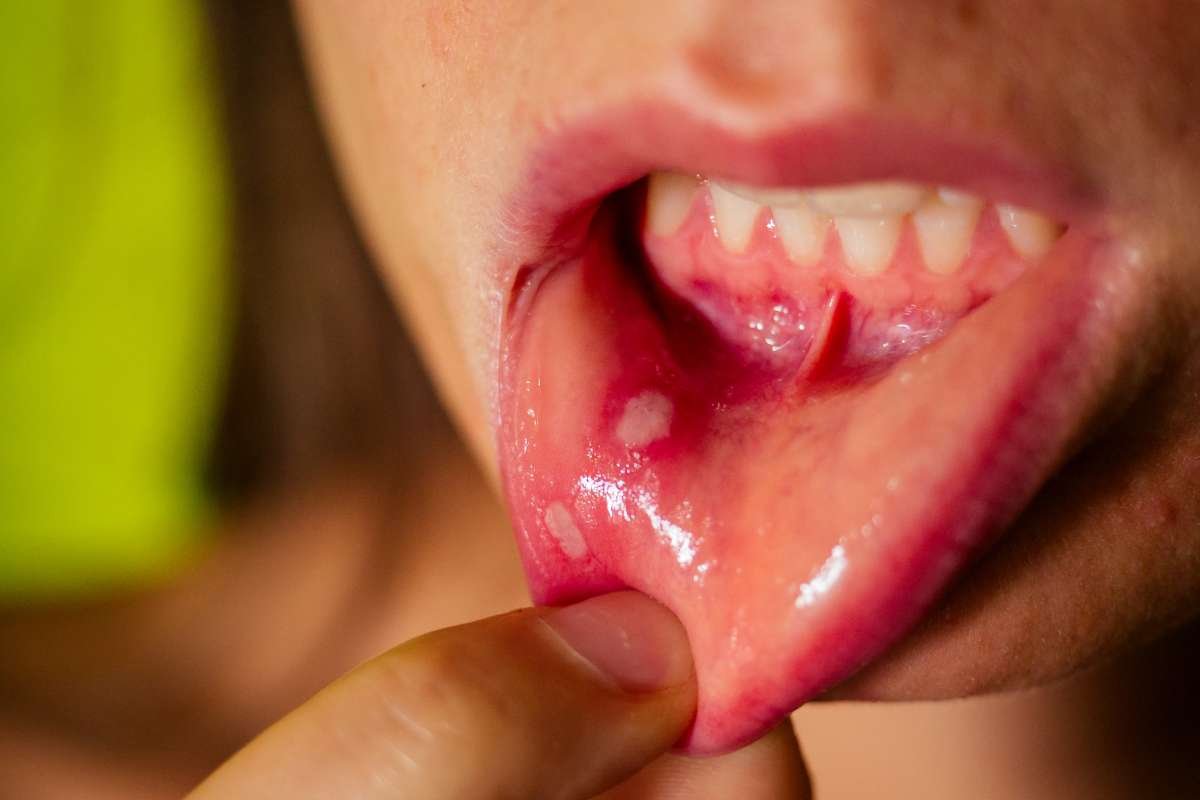

A yeast infection caused by Candida albicans, oral thrush can lead to creamy white patches on the tonsils, tongue, and roof of the mouth.
Symptoms:
- White lesions that can be scraped off
- Burning or soreness in the mouth
- Cracked corners of the mouth
- Loss of taste
6. Leukoplakia
Though rare, leukoplakia causes thickened white patches that cannot be scraped off. It’s often associated with tobacco use and may affect the tonsils.
Note: While leukoplakia isn’t usually cancerous, it can sometimes become precancerous. A healthcare provider should always examine persistent white patches.
Similar Articles:
- 8 Reasons Why Your Throat Burns
- Understanding Tonsil Stones: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
- Understanding Strep Throat: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and Home Remedies
Risk Factors and Who’s Most Affected
Certain individuals are more prone to developing white spots on tonsils due to underlying risk factors:
- Children and adolescents: Due to increased exposure in schools
- People with weakened immune systems: Including those with autoimmune disorders, undergoing chemotherapy, or on immunosuppressive medication
- Smokers and tobacco users: More prone to chronic tonsil irritation and leukoplakia
- Poor oral hygiene: Increases risk for tonsil stones and oral thrush
When to See a Doctor?
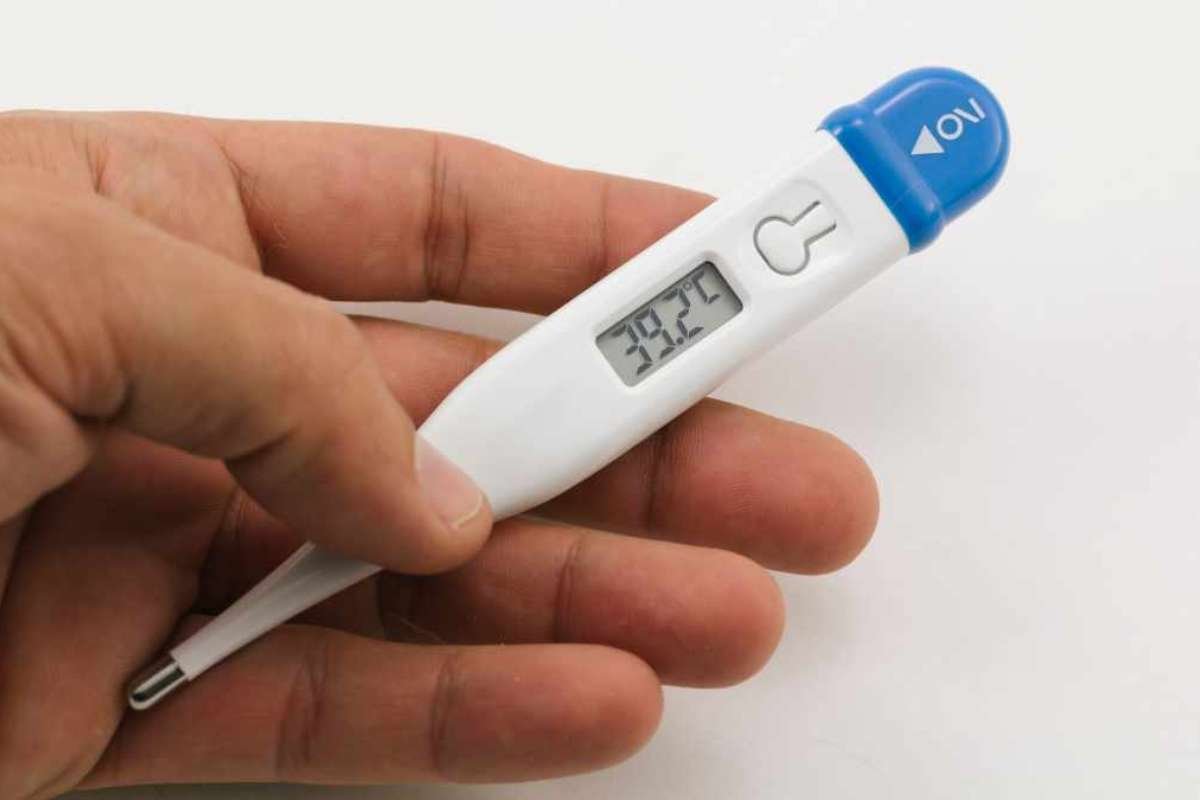
White spots on tonsils can sometimes clear up on their own, especially if caused by a mild viral infection. However, you should seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Fever above 101°F (38.3°C)
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- White spots lasting more than 4–5 days
- Severe sore throat with swollen glands
- Fatigue and body aches for more than a week
- Pus-filled tonsils or foul smell from the throat
Tip: Healthcare providers may use a rapid strep test or throat culture to confirm a diagnosis of strep throat. Blood tests might be ordered to rule out mononucleosis.
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider will typically perform a physical exam and may use the following diagnostic methods:
- Throat swab test: To detect bacterial infections like strep throat
- Blood tests: To check for viral infections like mono
- Oral swab: For detecting oral thrush
- Imaging (if needed): For deeper infections or persistent tonsil stones
Treatment Options
Treatment depends entirely on the underlying cause:
- Antibiotics: Used to treat bacterial infections such as strep throat or bacterial tonsillitis. Common antibiotics include amoxicillin or penicillin.
- Antiviral Medications: These may be prescribed for severe viral infections, although many viral cases resolve on their own with rest.
Antifungal Medications
For oral thrush, antifungal mouth rinses or tablets like nystatin or fluconazole may be used.

- Tonsil Stone Removal: Mild tonsil stones can be removed with a cotton swab or water flosser. Severe cases may require a minor surgical procedure.
- Hydration and Rest: Plenty of fluids, rest, and throat-soothing remedies like warm saltwater gargles or lozenges can ease symptoms in viral infections.
- Tonsillectomy: In chronic or severe cases, such as recurring tonsillitis or tonsil stones, a tonsillectomy (surgical removal of the tonsils) may be recommended.
Home Remedies to Manage Symptoms
While not a substitute for professional care, home remedies can relieve discomfort:
- Gargling with warm saltwater
- Drinking warm teas (chamomile or ginger)
- Using humidifiers to ease throat dryness
- Consuming honey for its antimicrobial properties
- Avoiding spicy or acidic foods during recovery
💡 Note: Always consult a doctor before starting any treatment—especially antibiotics or home remedies for children.
Prevention Tips
Preventing white spots on tonsils involves maintaining good overall hygiene and avoiding exposure to pathogens.
- Wash hands frequently
- Avoid sharing food or drinks
- Maintain oral hygiene: brushing and flossing twice daily
- Avoid smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- Strengthen your immune system with a healthy diet and sleep
Final Thoughts
White spots on tonsils often happen with different conditions, from mild viral infections to more serious bacterial or fungal infections. Sometimes, they go away on their own, but if symptoms stay or get worse, you should see a doctor.
Knowing the causes, what symptoms to look for, and acting quickly can help you or your loved ones get better faster and avoid problems.