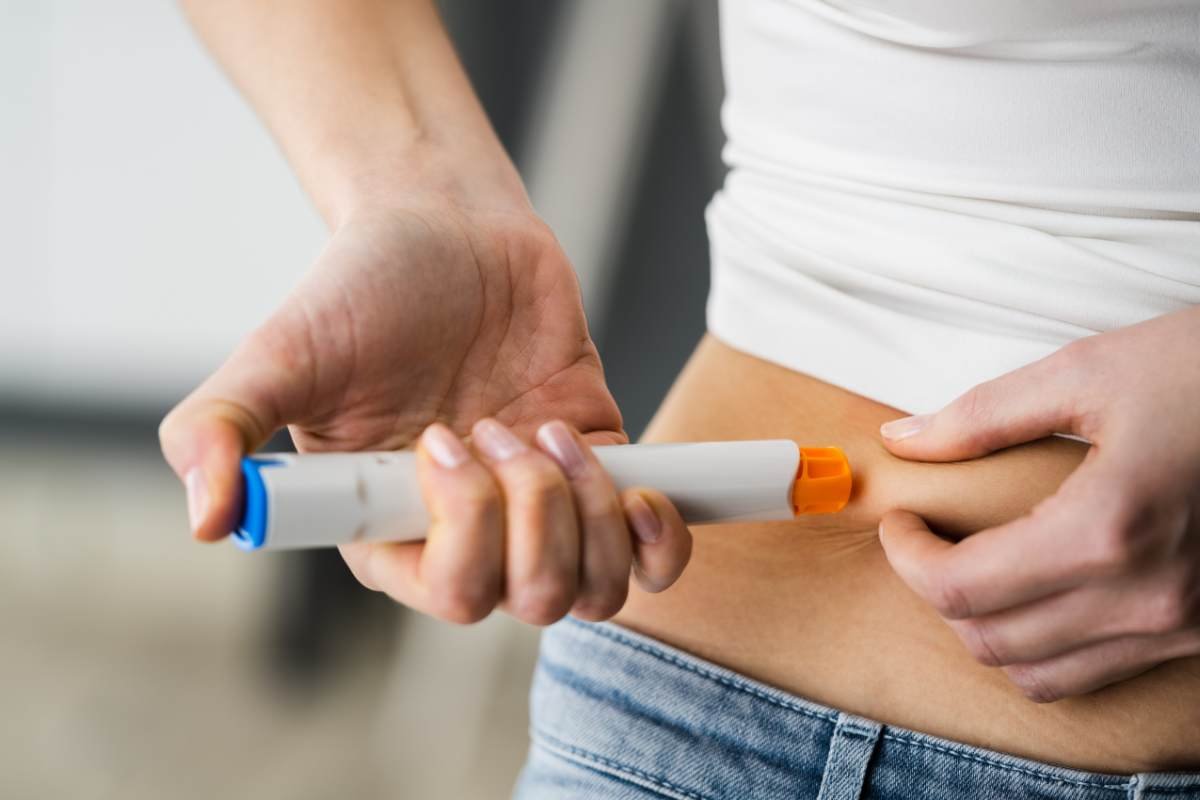
Modern healthcare is changing quickly, and one of the most important developments in recent years is the rise of self-injection systems. These clever devices have changed the way patients take care of their health by giving them more independence, making it more convenient, and helping them stick to their treatment plans better.
For millions of people with ongoing health issues like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or hormonal imbalances, these systems have made a big difference.
This article will explain what self-injection systems are, their benefits, the different types available, and how they are changing healthcare for both patients and doctors.
What Are Self-Injection Systems?
In simple terms, these systems are medical devices designed to allow patients to administer their medications safely and accurately without the need for a healthcare professional. These systems are particularly useful for people who require frequent injections as part of their treatment plan.
These systems are engineered to be user-friendly, even for individuals with minimal medical training. They typically come with ergonomic designs, clear instructions, and safety features to minimize risks such as needle-stick injuries or dosage errors.
Why Are Self-Injection Systems Important?
Before the advent of these systems, patients often had to visit clinics or hospitals for injections, which could be time-consuming, inconvenient, and costly. By enabling patients to take control of their treatments, these systems offer several significant advantages:
- Convenience: Patients can administer their medication anytime and anywhere, eliminating the need for frequent hospital visits.
- Improved Treatment Adherence: When treatments are easier to manage, patients are more likely to stick to their prescribed regimens, leading to better health outcomes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: These systems reduce the overall cost of treatment by cutting out recurring healthcare professional fees for administering injections.
- Empowerment: Giving patients the tools to manage their conditions fosters a sense of independence and confidence.
- Reduced Healthcare Burden: As more people use these systems, healthcare facilities can focus their resources on patients with more critical needs.
Also Read: Why Digital Twin Technology is the Future of Healthcare?
Common Uses of Self-Injection Systems
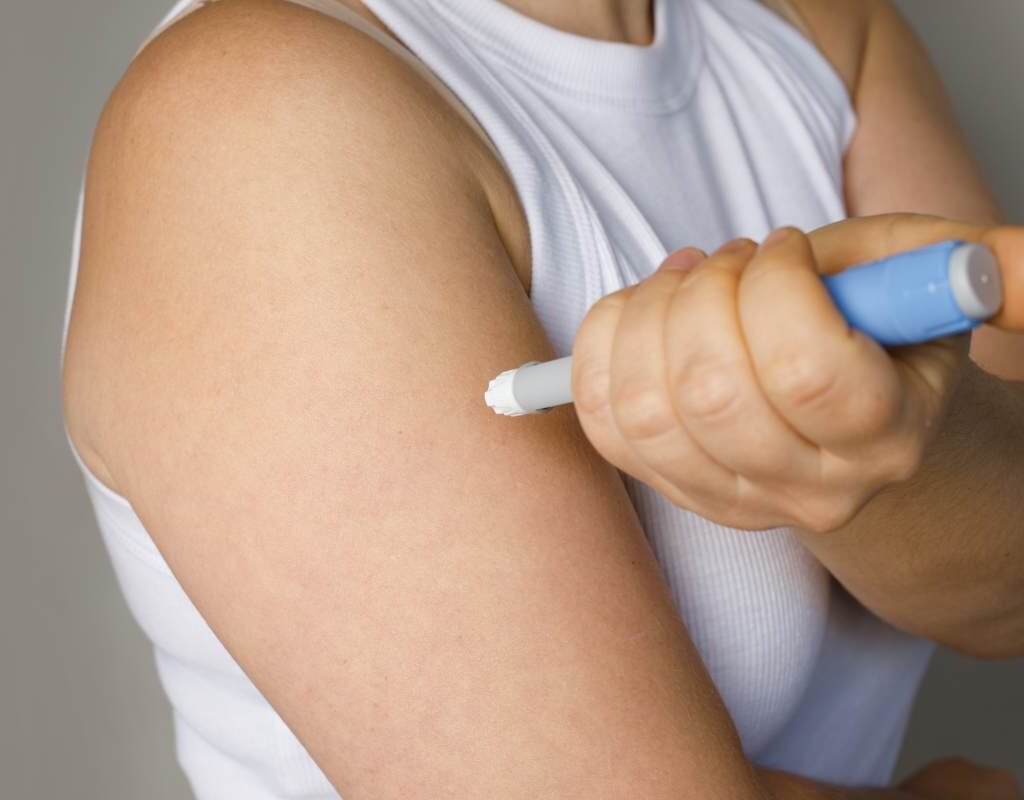
These systems are used across a wide range of medical conditions. Some of the most common applications include:
- Diabetes Management: Insulin pens and pumps are perhaps the most well-known type of self-injection systems. They help patients with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Medications like biologics, which reduce inflammation, are often administered through these systems.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Conditions like growth hormone deficiencies or hormonal imbalances often require regular injections, which are easily managed with these systems.
- Allergy Treatments: Epinephrine auto-injectors, such as EpiPens, are life-saving devices for individuals with severe allergies, allowing them to administer treatment during an emergency.
- Cancer Therapies: Some cancer treatments, such as specific immunotherapies, can be self-administered under medical guidance.
- Fertility Treatments: Women undergoing fertility treatments often use these systems for hormonal medications.
Also Read: Understanding the Key Differences and Similarities between Pharmaceutical vs Biotech
Types of Self-Injection Systems
- Auto-Injectors: Auto-injectors are pre-filled devices that deliver a single dose of medication. They are designed to be simple to use, often requiring just the press of a button to administer the injection. These are widely used for epinephrine, biologics, and other medications.
- Pen Injectors: Pen injectors, or insulin pens, are reusable or disposable devices commonly used for diabetes management. They are compact, portable, and allow users to adjust the dosage as needed.
- Prefilled Syringes: These are syringes preloaded with a specific dose of medication. While they may require manual injection, they are convenient and reduce the risk of dosage errors.
- Needle-Free Injectors: A newer innovation, needle-free injectors use high-pressure technology to deliver medication through the skin without a needle. These systems are ideal for patients with needle phobia.
- Wearable Injectors: Wearable self-injection systems are designed for longer-term treatments. These devices adhere to the skin and deliver medication over a set period, making them ideal for patients requiring continuous dosing.
How to Use Self-Injection Systems Safely
While these systems are designed to be user-friendly, proper usage is crucial to ensure safety and effectiveness. Here are some tips:
- Follow Instructions: Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions or guidelines provided by your healthcare provider.
- Practice Hygiene: Wash your hands and clean the injection site with an alcohol swab before administering the injection.
- Choose the Right Site: Common injection sites include the abdomen, thighs, or upper arms. Ensure you rotate sites to avoid irritation or scarring.
- Dispose of Needles Properly: Used needles should be disposed of in a designated sharps container to prevent injuries and environmental hazards.
- Get Training: If you’re new to self-injection systems, ask your doctor or nurse for a demonstration to ensure you’re comfortable and confident with the process.
Innovations in Self-Injection Systems
The world of these systems is always changing, with new improvements making these devices even better and easier to use. Here are some exciting advancements:
- Smart Self-Injection Systems: These devices now have Bluetooth technology, which lets them connect to mobile apps. This helps users track their medication schedules and get reminders when it’s time to take their medicine.
- Customizable Dosage Systems: Some advanced systems allow users to have better control over how much medication they take, making it easier to meet their specific needs.
- Eco-Friendly Designs: Many companies are working on creating systems that can be reused or are made from biodegradable materials to help reduce medical waste.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Newer systems include features like automatic needle retraction and other safety measures to lower the risk of accidents.
Challenges and Considerations
While these systems offer numerous benefits, there are some challenges to consider:
- Needle Phobia: Some patients may struggle with self-injection due to a fear of needles. Needle-free systems are helping to address this issue.
- Learning Curve: New users may take time to become comfortable with the devices, requiring adequate training and support.
- Cost: The initial expense of these systems can be a barrier for some patients, although long-term savings often outweigh the upfront cost.
- Storage and Handling: Certain medications require specific storage conditions, such as refrigeration, which can be inconvenient for some users.
The Future of Self-Injection Systems
The future of these systems looks promising, with ongoing research and development focused on improving ease of use, safety, and accessibility. As more patients embrace these systems, the demand for innovative solutions will continue to grow.
One area of focus is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics into these systems. These advancements could enable devices to monitor a patient’s health in real-time, adjust dosages automatically, and even alert healthcare providers in case of anomalies.
Additionally, efforts are being made to make these systems more affordable and accessible to patients in low-income regions, ensuring that everyone can benefit from this transformative technology.
Also Read: Understanding the Difference between EHR and EMR and Their Unique Roles in Healthcare
Conclusion
Self-injection systems are changing healthcare by giving patients more control over their treatments. Whether it’s managing chronic conditions like diabetes or giving important medications during emergencies, these devices make medical care easier, more efficient, and focused on the patient.
As technology keeps improving, these systems will become even more advanced, providing greater benefits to patients around the world. If you’re thinking about using a self-injection system, talk to your doctor to find the best option for your needs. With the right training and support, these systems can greatly improve your quality of life and make it easier to manage your health condition.
By understanding how these systems work, we can see how they are influencing the future of healthcare—helping patients feel more independent and confident.