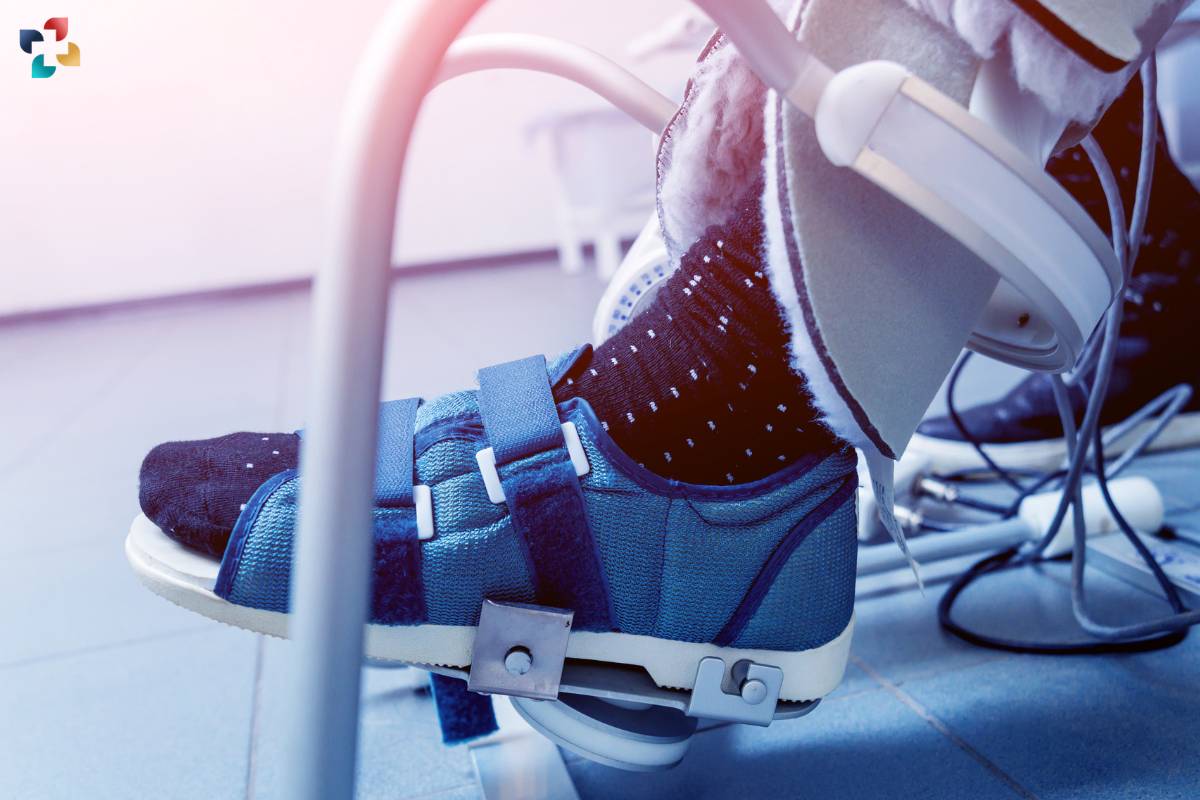
Continuous Passive Motion (CPM) therapy is a widely used rehabilitation technique aimed at enhancing joint recovery and mobility after surgery or injury. This therapy involves the continuous and controlled movement of a joint through a predetermined range of motion using a specialized CPM machine. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the principles, benefits, applications, and considerations associated with Continuous Passive Motion therapy.
Understanding Continuous Passive Motion
Continuous Passive Motion, as the name suggests, involves the passive movement of a joint without any active effort from the patient. The joint is moved gently and continuously through a controlled range of motion, such as flexion and extension, typically in a repetitive manner. CPM therapy is commonly used for joints such as the knee, shoulder, elbow, wrist, and ankle.
Continuous Passive Motion (CPM) therapy is a well-established rehabilitation technique that has been used for decades to promote joint recovery and mobility. The concept of CPM therapy is based on the principle of controlled passive movement, where the joint is moved through its range of motion without any active participation from the patient. This gentle and continuous movement helps prevent joint stiffness, adhesion formation, and contractures, which are common complications following surgery or injury.
CPM therapy is typically initiated shortly after surgery or trauma when the joint is still healing and may be vulnerable to stiffness or immobility. By providing controlled movement to the joint, CPM therapy helps stimulate circulation, enhance synovial fluid production, and promote tissue healing. Additionally, CPM therapy helps improve proprioception, which is the body’s ability to sense joint position and movement, aiding in neuromuscular re-education and motor control.
One of the key advantages of CPM therapy is its versatility, as it can be used for a wide range of joints, including the knee, shoulder, elbow, wrist, and ankle. This makes it a valuable tool in orthopedic and sports medicine rehabilitation, where maintaining joint mobility and function is essential for optimal recovery.
Overall, Continuous Passive Motion therapy is a safe and effective modality for promoting joint healing and mobility, particularly in the early stages of rehabilitation. When combined with other modalities such as physical therapy and therapeutic exercises, CPM therapy can help accelerate recovery and improve functional outcomes for patients recovering from joint surgery or injury.
Principles of Continuous Passive Motion
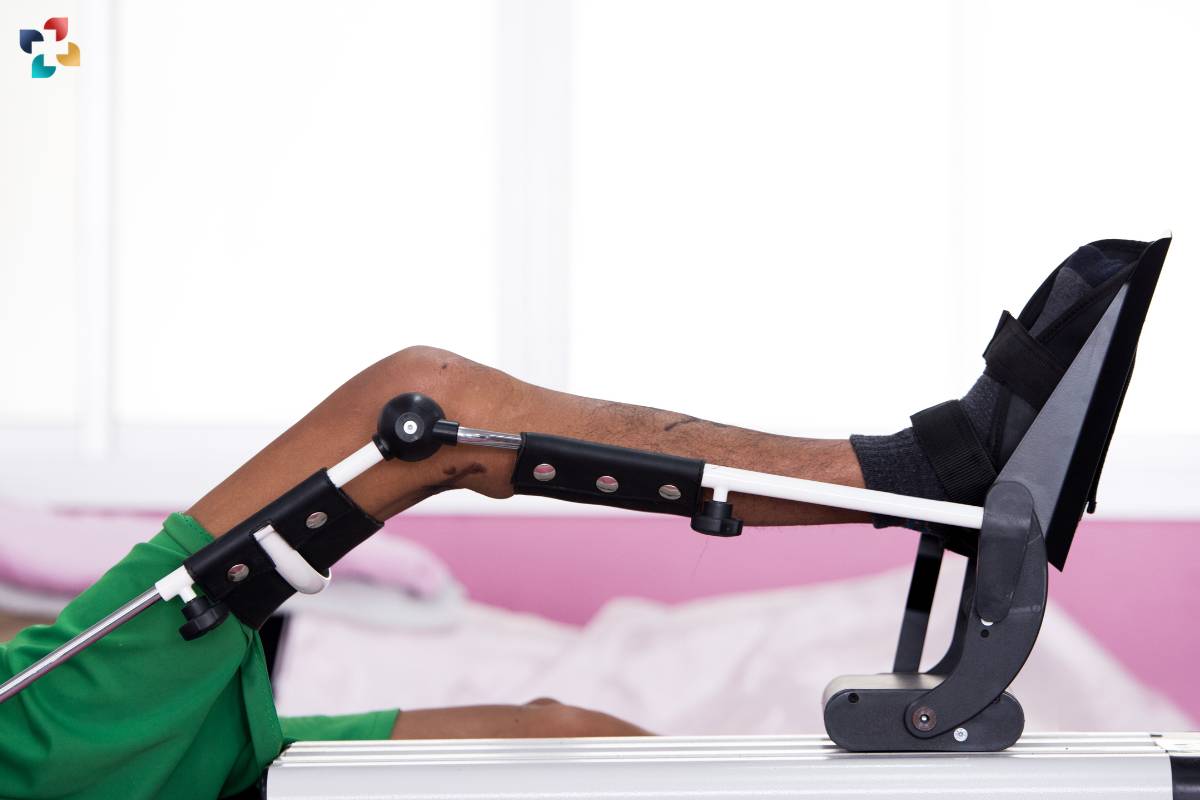

The primary principle behind Continuous Passive Motion therapy is to promote early joint mobilization and prevent stiffness and adhesion formation following surgery or injury. By providing controlled movement to the joint, CPM therapy helps improve circulation, reduce swelling, enhance synovial fluid production, and prevent scar tissue formation. Additionally, CPM therapy promotes proprioception, which is the body’s awareness of its position in space, facilitating neuromuscular re-education and motor control.
Benefits of Continuous Passive Motion:
Continuous Passive Motion therapy offers a myriad of benefits for patients undergoing rehabilitation:
1. Facilitates Joint Healing
CPM therapy helps promote the healing process by stimulating the production of synovial fluid, which nourishes the joint cartilage and facilitates the removal of metabolic waste products.
2. Improves Range of Motion
By gently moving the joint through its full range of motion, CPM therapy helps prevent joint stiffness and contractures, allowing for quicker recovery of functional mobility.
3. Reduces Pain and Swelling
The rhythmic movement provided by CPM therapy helps alleviate pain and swelling associated with surgery or injury, promoting patient comfort and compliance with rehabilitation protocols.
4. Prevents Adhesion Formation
Continuous passive movement helps prevent the formation of adhesions or scar tissue within the joint capsule, which can restrict joint movement and impair function.
5. Enhances Rehabilitation Outcomes
Incorporating CPM therapy into the rehabilitation protocol has been shown to improve functional outcomes, accelerate recovery, and shorten hospital stays for patients undergoing joint surgery or trauma.
Applications of Continuous Passive Motion:
Continuous Passive Motion therapy finds applications in various orthopedic and sports medicine settings, including:
1. Postoperative Rehabilitation
CPM therapy is commonly used following orthopedic surgeries such as knee arthroplasty (joint replacement), ACL reconstruction, meniscal repair, shoulder surgery, and elbow surgery to promote early joint mobilization and optimize surgical outcomes.
2. Trauma Rehabilitation
CPM therapy may be employed in the management of acute joint injuries such as ligament sprains, muscle strains, and fractures to facilitate early mobilization and prevent secondary complications.
3. Sports Injury Rehabilitation
Athletes recovering from sports-related injuries, such as ligament tears, tendonitis, or cartilage damage, may benefit from CPM therapy to expedite the healing process and restore optimal joint function.
Considerations for Continuous Passive Motion Therapy:
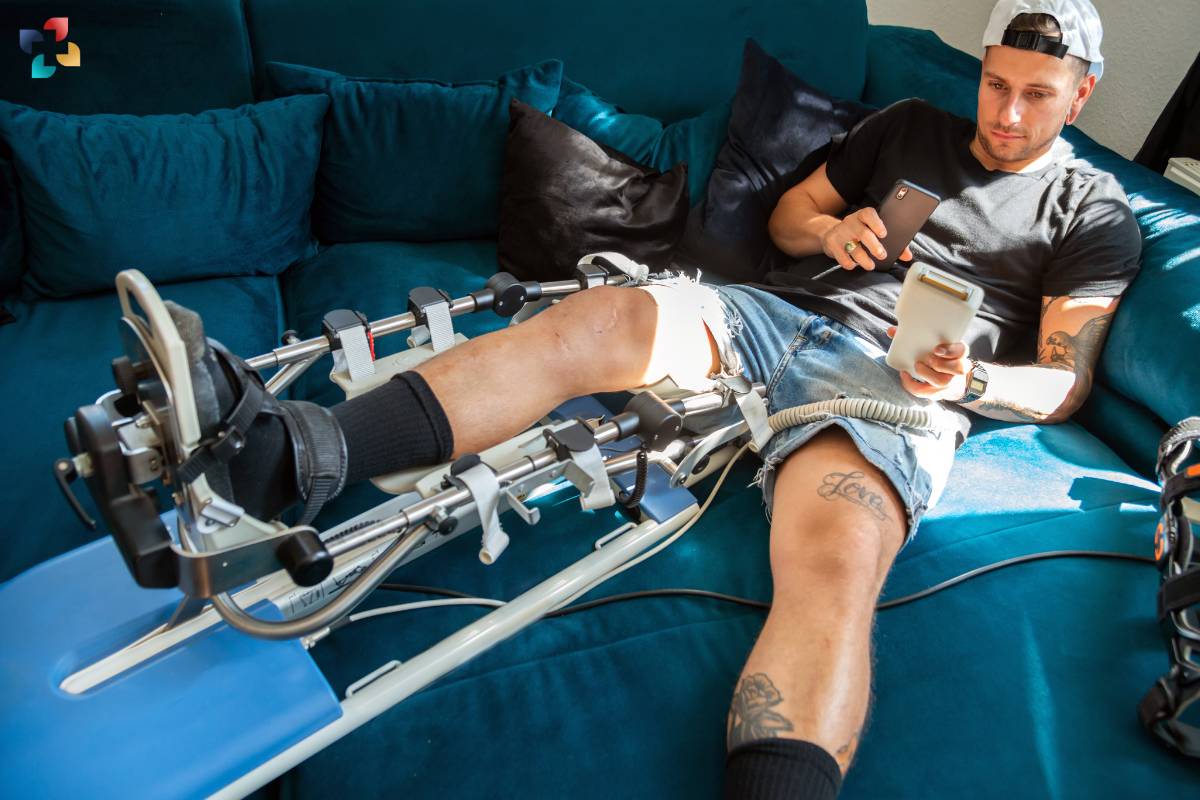
While Continuous Passive Motion therapy offers numerous benefits, several considerations should be taken into account:
1. Patient Selection
CPM therapy may not be suitable for all patients, particularly those with certain medical conditions, joint instability, or contraindications to movement. A thorough assessment by a qualified healthcare professional is essential to determine the appropriateness of CPM therapy for each patient.
2. Optimal Parameters
The parameters of CPM therapy, including range of motion, speed, and duration of treatment, should be tailored to the individual patient’s needs and tolerance levels. Close monitoring and adjustment of these parameters are necessary to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
3. Adjunctive Therapies
CPM therapy is most effective when combined with other modalities such as physical therapy, manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and modalities like ice or heat therapy. A multimodal approach to rehabilitation ensures comprehensive care and maximizes functional recovery.
4. Compliance and Education
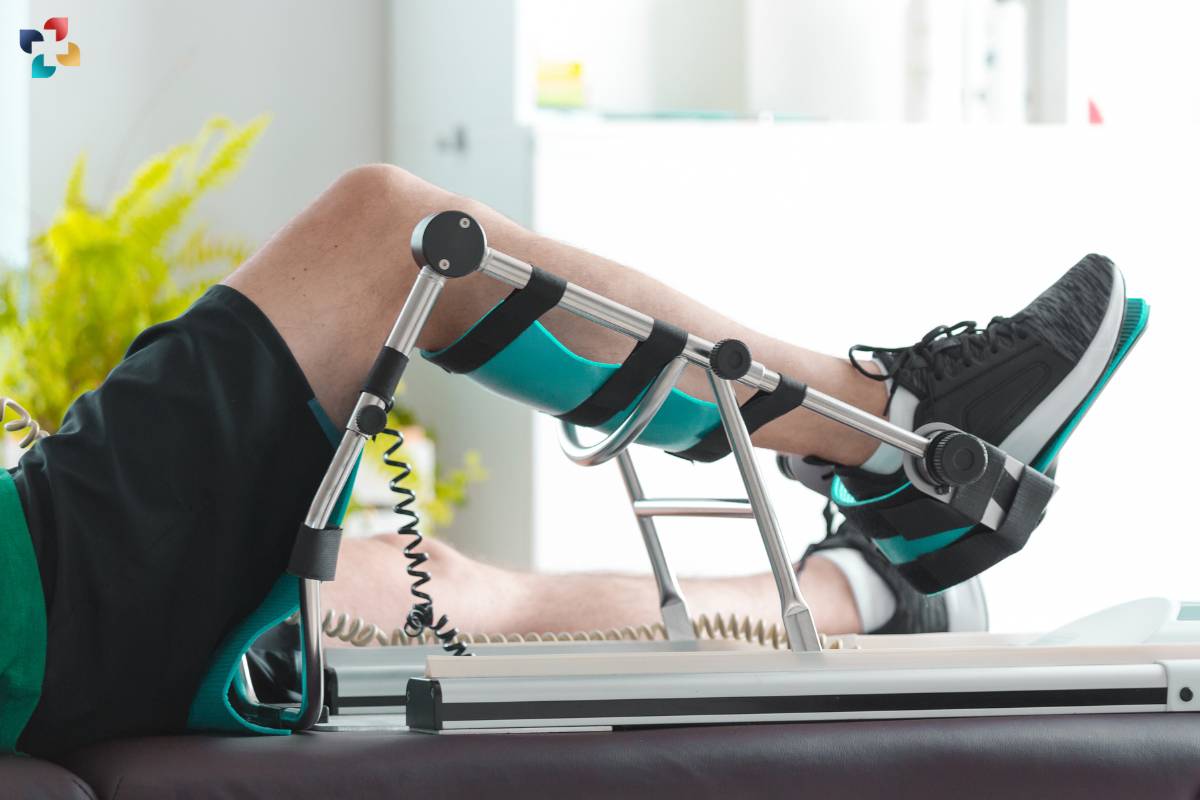

Patient education and compliance play a crucial role in the success of CPM therapy. Patients should be adequately informed about the purpose, benefits, and expectations of CPM therapy, as well as proper positioning and use of the CPM machine to ensure safe and effective treatment delivery.
Conclusion
Continuous Passive Motion therapy is a valuable adjunctive modality in orthopedic and sports medicine rehabilitation, offering numerous benefits for patients recovering from joint surgery or injury. By promoting early joint mobilization, preventing stiffness and adhesion formation, and facilitating optimal healing, CPM therapy plays a vital role in enhancing functional outcomes and expediting the return to activity. However, careful patient selection, individualized treatment parameters, and comprehensive rehabilitation strategies are essential to maximize the effectiveness of CPM therapy and optimize patient outcomes.







