Study Reveals the Importance of Ancient Trees
A recent study led by the University of Barcelona sheds light on the critical role played by the oldest trees in protecting endangered species in forest ecosystems. Published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA (PNAS), the study underscores how preserving ancient trees is essential for biodiversity conservation amid the challenges posed by global environmental changes.
Ancient Trees Provide Shelter for Endangered Species
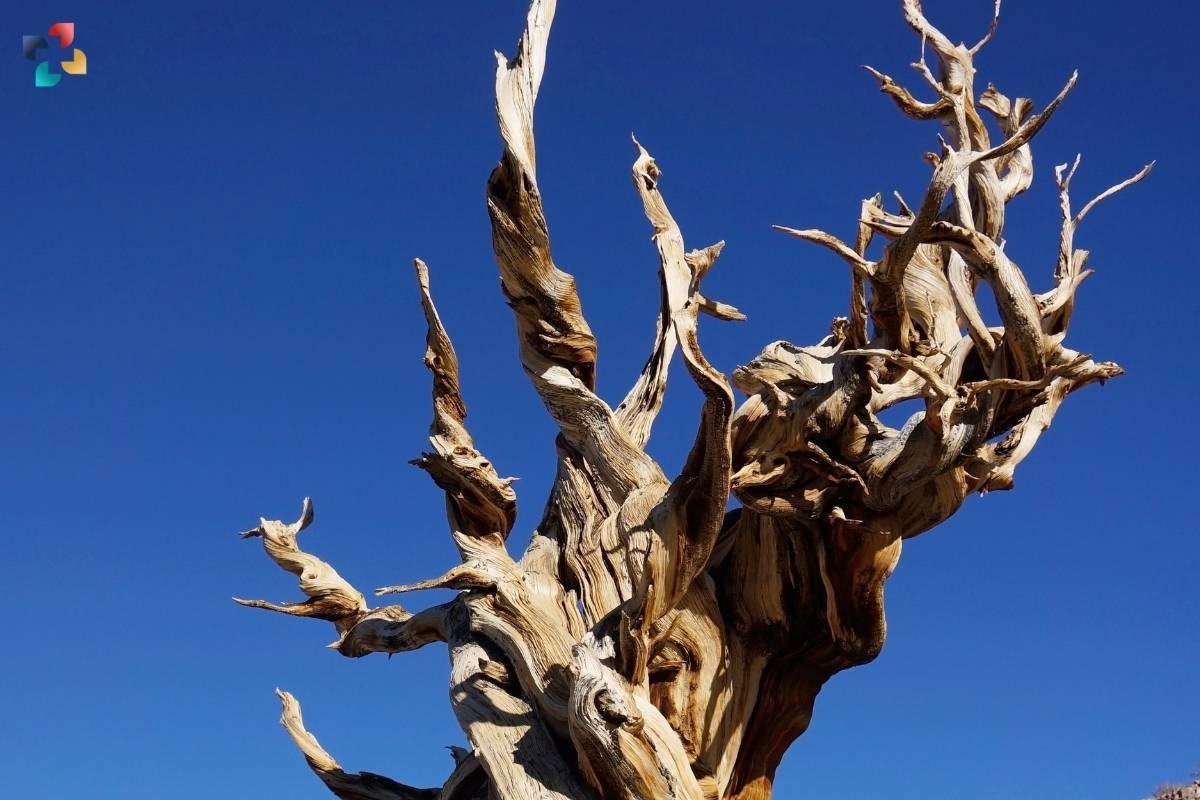
The research focuses on the wolf lichen (Letharia vulpina), an endangered species prevalent in mature forests and long-lived trees. Specifically, the study highlights the symbiotic relationship between the wolf lichen and the oldest trees, such as the black pine (Pinus uncinata) in the high mountains of the Pyrenees. These ancient trees serve as life shelters for the wolf lichen, offering unique physiological characteristics and habitats conducive to its survival.
Threats to Ancient Trees and Conservation Efforts
While ancient trees play a crucial role in supporting biodiversity, they face threats from human activities, particularly deforestation. The study emphasizes the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect these majestic trees and the species that depend on them for survival. Researchers emphasize the interconnectedness of all living beings and stress the importance of respecting nature to preserve biodiversity and ecosystems for future generations.
Conclusion
The study underscores the significance of ancient trees in safeguarding endangered species and highlights the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect these vital ecosystems. By recognizing the ecological importance of ancient trees and taking proactive measures to preserve them, we can contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and ensure the long-term health of forest ecosystems.