Source – Neuroscience News
Nestled within the intricate labyrinth of the human body lies a remarkable frontier – the blood-brain barrier (BBB). This selective gatekeeper stands guard between the gushing torrent of our bloodstream and the delicate ecosystem of the brain. Unlike most tissues, the brain doesn’t readily embrace everything circulating in our blood. It demands a high level of security, a filter to ensure only essential substances gain entry, and potentially harmful intruders are kept at bay. Understanding this fascinating barrier is akin to deciphering a secret code, unlocking the mysteries of how our brains stay protected and function optimally.
What is the Blood-Brain Barrier?
Imagine a tightly woven net lining the blood vessels within the brain. This specialized network of endothelial cells, along with supporting proteins and tight junctions, forms the formidable blood-brain barrier. Unlike leaky vessels elsewhere in the body, the BBB strictly regulates what passes through, acting as a vigilant sentry safeguarding the brain’s sensitive environment.
Imagine this net isn’t just static; it’s a dynamic fortress constantly adapting to its environment. It possesses its own unique language, communicating with neighboring cells and regulating its own permeability. Tight junctions, like microscopic drawbridges, control the flow of molecules, opening and closing in response to specific signals. Embedded proteins act as meticulous inspectors, scrutinizing each molecule seeking entry, granting passage only to those deemed essential for the brain’s delicate symphony.
This intricate dance between control and communication allows the BBB to maintain a carefully orchestrated internal environment. It’s a selective shield, not an impenetrable wall, ensuring the brain has access to vital resources while keeping out potential threats. This constant balancing act, this ongoing conversation between blood and brain, is what truly defines the remarkable nature of the blood-brain barrier.
Three Crucial Functions of the Blood-Brain Barrier:
1. Protection
The BBB shields the brain from potentially harmful substances. Toxins, pathogens, and even some medications can wreak havoc on delicate neurons. The BBB acts as a shield, filtering out these unwanted intruders and maintaining a stable internal environment for optimal brain function.
2. Nutrient Delivery
While excluding harmful substances, the Blood-Brain Barrier selectively allows essential nutrients and molecules to nourish the brain. Glucose, amino acids, and specific ions like potassium and calcium readily traverse the barrier, ensuring the brain has the fuel and building blocks it needs to thrive.
3. Homeostasis
The BBB plays a crucial role in maintaining the brain’s chemical and electrical balance. It regulates the influx and efflux of ions, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules, ensuring a stable internal environment for proper neuronal communication and cognitive function.
Also Read: Should You Be Worried About a Brain Aneurysm? Understanding the Risks and Taking Precautions
What Does the Blood-Brain Barrier Let Through?
Not all molecules hold the golden ticket to the brain’s VIP lounge. Certain properties act as secret passwords, granting them swift passage through the BBB’s selective checkpoint. Lipophilicity, like a magic cloak of fat, allows hormone messengers and some medications to seamlessly blend in with the lipid membranes of the endothelial cells, slipping through unnoticed. Size also matters; smaller molecules like glucose, the brain’s primary fuel, and essential amino acids for building proteins, can effortlessly squeeze through the microscopic gaps between tightly knit junctions.
But for some, brute force isn’t enough. Dedicated transport proteins, acting as meticulous bouncers, recognize specific molecules vital for brain function, like ions and neurotransmitters, and usher them through designated entryways, ensuring the brain receives the essential resources it needs to thrive.
This intricate system of checkpoints and privileged access underscores the remarkable selectivity of the Blood-Brain Barrier, meticulously safeguarding the brain’s delicate ecosystem.
1. Lipophilicity
Fat-soluble molecules like certain hormones and some medications can readily slip through the lipid membranes of the endothelial cells.
2. Small size
Smaller molecules, like glucose and amino acids, can squeeze through the tight junctions between endothelial cells.
3. Specific transporters
Dedicated transport proteins act as gatekeepers, selectively ushering in essential nutrients and molecules like ions and neurotransmitters.
What Cannot Pass the Blood-Brain Barrier?
While some molecules waltz through the BBB, others face a brick wall:
1. Large molecules
Proteins and complex sugars are simply too bulky to navigate the tight junctions.
2. Water-soluble molecules
Charged molecules that don’t readily dissolve in lipids find it challenging to cross the BBB’s fatty membrane.
3. Toxins and pathogens
Most toxins and pathogens lack the necessary properties to bypass the BBB, protecting the brain from their harmful effects.
The BBB’s Significance in Health and Disease:
Understanding the BBB’s function is crucial in various aspects of health and disease:
1. Drug delivery
Developing drugs that can effectively cross the Blood-Brain Barrier is a major challenge in treating brain-related diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Research focuses on strategies to bypass the barrier or create drug delivery systems that can navigate its intricacies.
2. Brain tumors
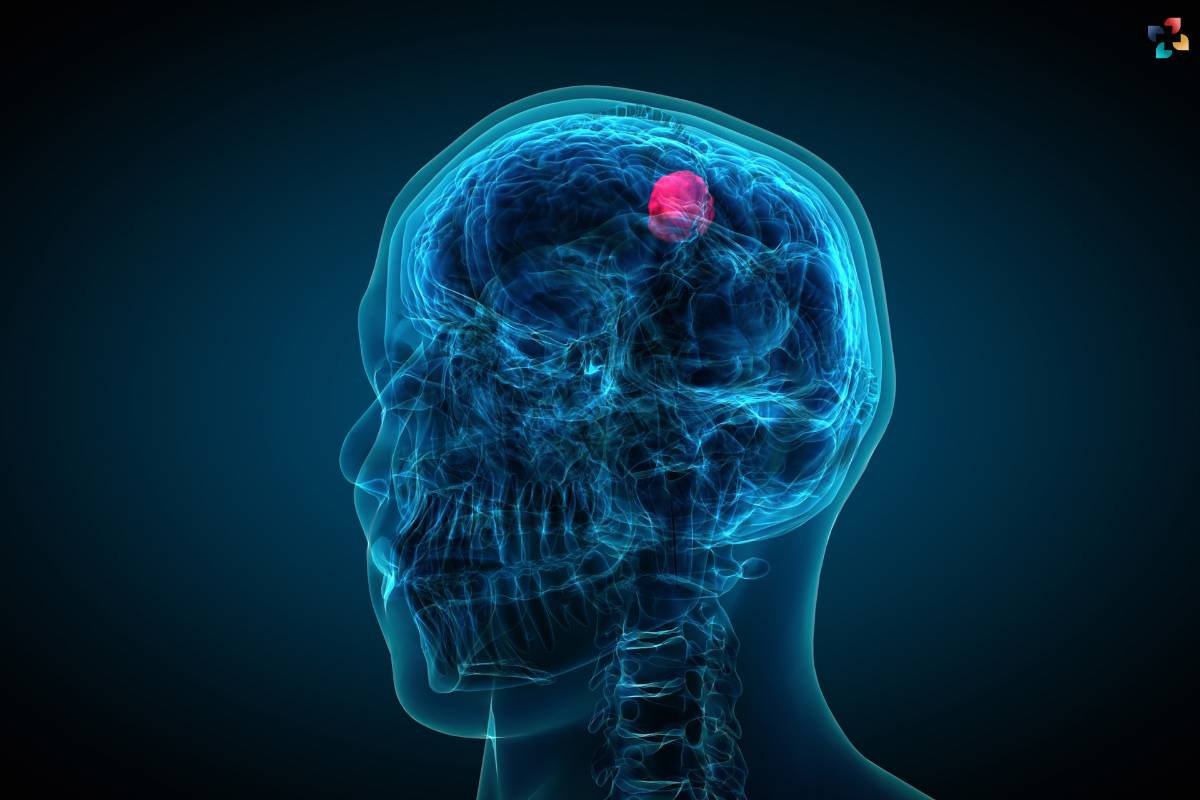
The BBB can also pose a challenge in treating brain tumors. Some cancer drugs struggle to reach the tumor due to the barrier’s filtering mechanisms. Researchers are exploring ways to manipulate the BBB to improve drug delivery and tumor targeting.
3. Neurological disorders
Conditions like Alzheimer’s and multiple sclerosis involve disruptions in the BBB’s function, potentially contributing to the progression of these diseases. Understanding these disruptions could lead to novel therapeutic approaches.
The Future of the Blood-Brain Barrier:
The BBB, once considered an impenetrable fortress, is now actively being explored and manipulated. Research into its structure, function, and potential vulnerabilities holds immense promise for developing targeted therapies for neurological and neurodegenerative diseases. As we unlock the secrets of this remarkable gatekeeper, we pave the way for a future where protecting and nurturing the brain takes center stage in healthcare.







