The flu is a common respiratory illness caused by the influenza virus. Despite being a widely recognized illness, there are several myths and misconceptions about the flu. Some of these myths are harmless, but others can be dangerous, leading people to make incorrect assumptions about the flu and how to prevent or treat it. In this article, we will explore 12 common flu myths and bust them using scientific evidence.
Here are 12 Flu Myths Busted:
Flu Myth 1: The flu is just a bad cold
Fact: The flu and the common cold are caused by different viruses. Although they share some symptoms such as cough, fever, and sore throat, the flu is more severe and can lead to complications such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinus infections. In some cases, the flu can even lead to death.
Flu Myth 2: The flu vaccine can give you the flu

Fact: The flu vaccine cannot give you the flu. The vaccine is made from inactivated or weakened flu viruses that cannot cause illness. Some people may experience mild side effects such as soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site, low-grade fever, or muscle aches after getting the vaccine. However, these side effects are not the same as getting the flu.
Flu Myth 3: You don’t need a flu shot every year
Fact: The flu virus changes every year, so the vaccine needs to be updated annually to protect against the most common strains. The protection from the flu vaccine can also decrease over time, so getting a shot every year is recommended.
Flu Myth 4: You can get the flu from the vaccine
Fact: The flu vaccine cannot give you the flu because it is made from inactivated or weakened viruses that cannot cause illness. It is possible to catch the flu shortly after getting the vaccine, but this is not because of the vaccine itself. It takes about two weeks for the vaccine to become effective, and people can still catch the flu during that time.
Flu Myth 5: Antibiotics can cure the flu
Fact: Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections, not viral infections like the flu. The flu is caused by a virus, and antibiotics cannot cure it. Antiviral medications may be prescribed to treat the flu, but they work best when taken within 48 hours of the onset of symptoms.
Flu Myth 6: You can catch the flu from going outside with wet hair
Fact: Going outside with wet hair cannot give you the flu. The flu is a viral infection that is spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes. The only way to catch the flu is by coming into contact with the virus.
Flu Myth 7: You can’t spread the flu if you feel fine
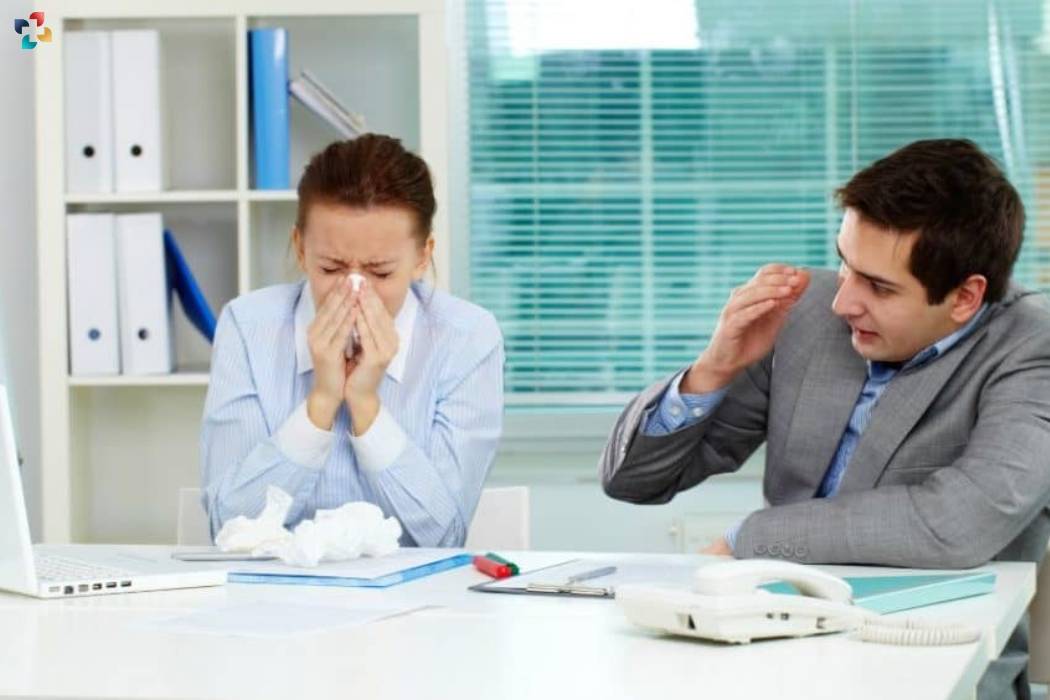

Fact: People infected with the flu can spread the virus even if they feel fine. They may not have any symptoms yet, but they can still transmit the virus to others. This is why it is important to practice good hygiene habits such as washing your hands frequently, covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and staying home if you are sick.
Flu Myth 8: You can’t get the flu if you got the vaccine
Fact: Although the flu vaccine is effective, it is not 100% effective. It is still possible to catch the flu even if you got the vaccine, but the severity of the illness is usually milder, and the risk of complications is reduced. The vaccine can also reduce the spread of the flu in the community by increasing the number of people who are immune to the virus.
Flu Myth 9: The flu is only dangerous for the elderly
Fact: While the elderly are at higher risk for complications from the flu, anyone can get sick from the virus. Children, pregnant women, people with weakened immune systems, and those with underlying health conditions are also at higher risk for complications. It is important for everyone to take precautions to prevent the spread of the flu, regardless of age.
Flu Myth 10: You should take antibiotics for the flu
Fact: Antibiotics are not effective against the flu because the flu is caused by a virus, not bacteria. Taking antibiotics unnecessarily can contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which is a serious public health concern. Antiviral medications may be prescribed to treat the flu, but they are only effective if taken within the first 48 hours of symptoms.
Flu Myth 11: Natural remedies can cure the flu

Fact: While some natural remedies such as staying hydrated, getting plenty of rest, and using a humidifier can help alleviate flu symptoms, there is no cure for the flu. Antiviral medications may be prescribed to treat the flu, but they work best when taken within the first 48 hours of symptoms. It is important to consult a healthcare provider for appropriate treatment options.
Flu Myth 12: The flu is not a serious illness
Fact: The flu can be a serious illness, especially for people at higher risk for complications. It can lead to hospitalization, pneumonia, and even death. It is important to take precautions to prevent the spread of the flu, such as getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene habits, and staying home if you are sick.
BOTTOM LINE
There are several myths and misconceptions about the flu that can lead to incorrect assumptions about the illness and how to prevent or treat it. It is important to rely on scientific evidence and consult healthcare professionals for accurate information about the flu. Taking precautions such as getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene habits, and staying home if you are sick can help prevent the spread of the flu and protect yourself and others from the illness.
Also Read: 7 Helpful Home Remedies for the Flu